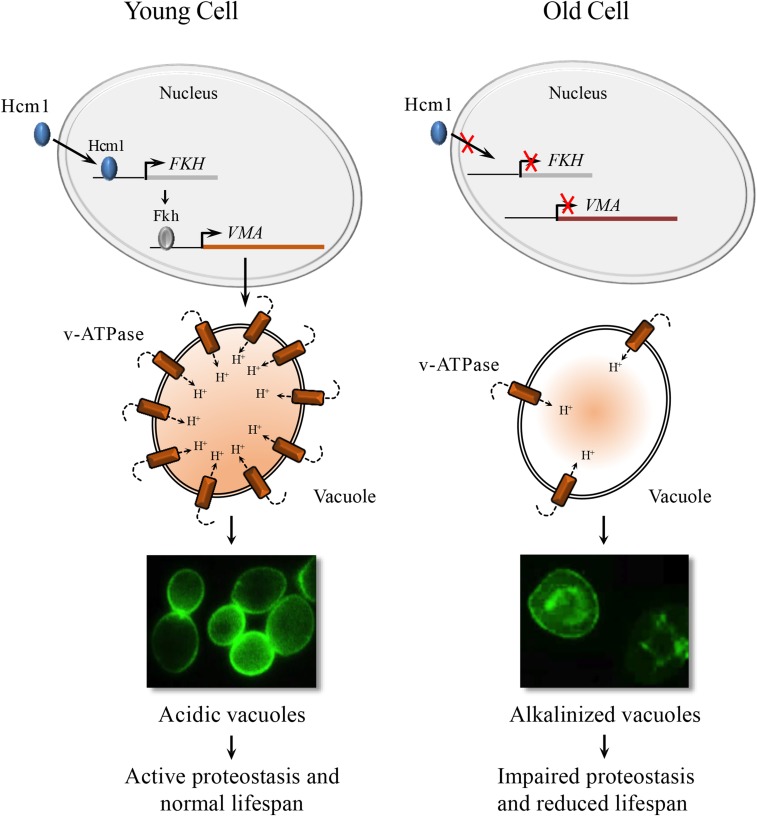
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of control of vacuolar acidity in aging yeast cells. A working model of an interconnected transcriptional network underlying vacuolar acidity in yeast. Nuclear localization of Hcm1 upregulates the expression of FKH genes in S/G2, which, in turn, induces the expression of VMA vacuolar proton pump genes in cells undergoing early divisions. Hcm1 is no longer restricted to the nucleus in replicatively old cells. This results in reduced expression of VMA genes and the ensuing loss of vacuolar acidity.