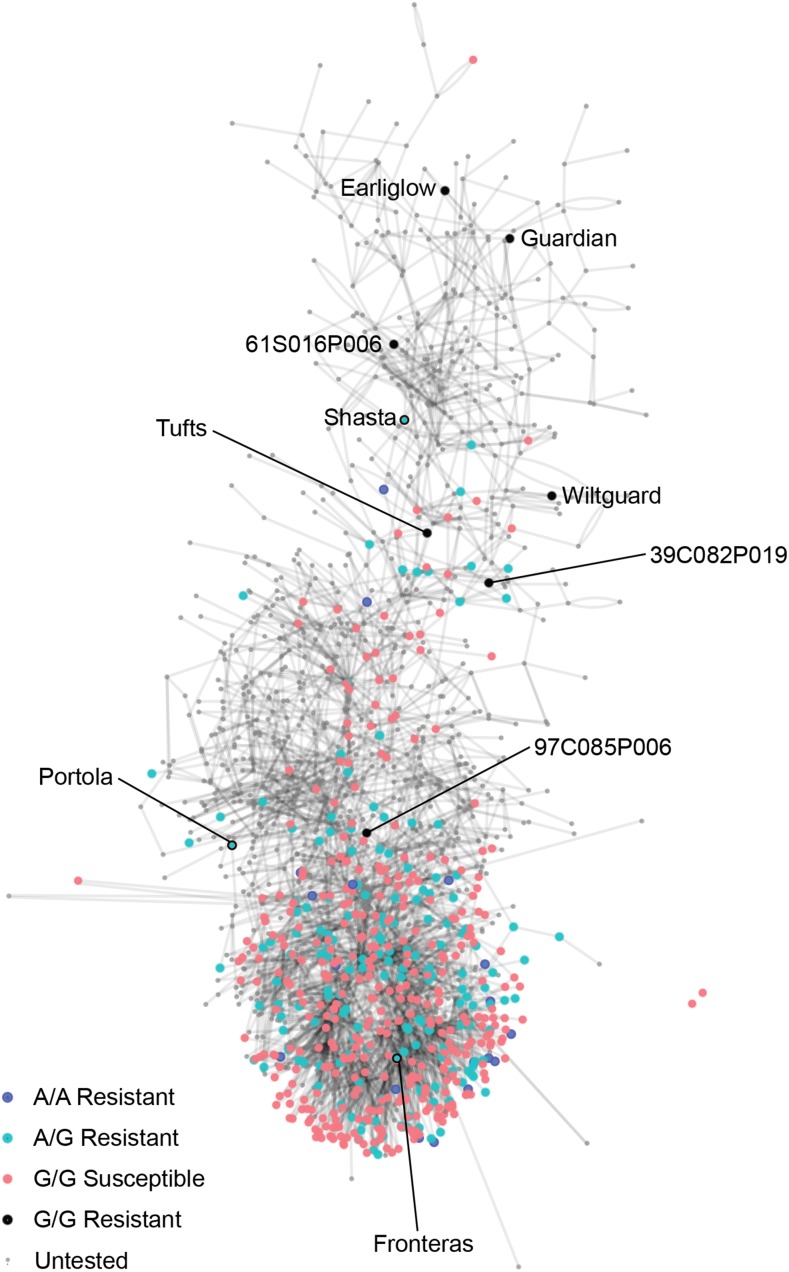
Figure 7.
Pedigree network for 1,663 F. × ananassa germplasm accessions with birth years ranging from 1814 to 2012. The north to south orientation of the network is approximately chronological. The pedigree records are supplied in Supplemental File 5. Nodes represent germplasm accessions, whereas connecting lines represent first-degree relatives (parent-offspring). The color of the node signifies a combination of the Fusarium wilt resistance phenotype and the AX-166521396 SNP marker genotype for 565 germplasm accessions. The other 1,098 germplasm accessions in the pedigree network were untested (small light gray nodes). The AX-166521396 SNP marker was in linkage disequilibrium with the Fw1 gene conferring resistance to Fusarium wilt. The A allele was associated with the resistant allele (Fw1), whereas the G allele was associated with the susceptible allele (fw1). AX-166521396 SNP marker genotypes predicted Fusarium wilt resistance phenotypes in 97% of the germplasm accessions tested: most A/A and A/G genotypes were resistant (blue and cyan filled circles, respectively), whereas most G/G genotypes were susceptible (salmon filled circles). Seven G/G genotypes were resistant and predicted to carry novel Fusarium wilt resistance genes (black filled circles).