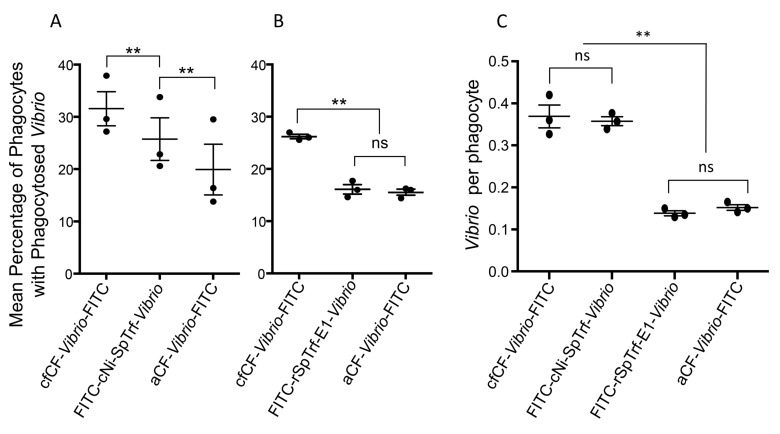
Fig 4. cNi-SpTrf proteins augment phagocytosis whereas rSpTrf-E1 proteins do not.
A. Opsonized Vibrio diazotrophicus was incubated with phagocytes for 70 min followed by fixing, staining, and analysis of the mean percentage of phagocytes (n = 500) that contained V. diazotrophicus. cNi-SpTrf proteins from three different sea urchins were evaluated for opsonization. Phagocytes were obtained from a sea urchin that was different from those that provided the cNi-SpTrf proteins or the cfCF used for opsonization. The percentage of phagocytes with FITC-cNi-SpTrf-Vibrio is intermediate between number of phagocytes with cfCF-Vibrio-FITC (positive control) and aCF-Vibrio-FITC (buffer control) (see Table 1 for definitions of the abbreviations). B. Opsonization of V. diazotrophicus with SpTrf proteins (cfCF-Vibrio-FITC) isolated from three sea urchins results in a greater percentage of phagocytes with bacteria than either FITC-SpTrf-E1-Vibrio or aCF-Vibrio-FITC. C. Vibrio diazotrophicus opsonized with cNi-SpTrf, rSpTrf-E1, cfCF or aCF were incubated with coelomocytes at a ratio of 100 bacteria per phagocyte. Phagocytosis of FITC-cNi-SpTrf-Vibrio results in similar numbers of V. diazotrophicus per phagocyte compared to cfCF-Vibrio-FITC, and both show significantly greater numbers of bacteria per phagocyte than aCF-Vibrio-FITC. Phagocytosis of FITC-SpTrf-E1-Vibrio results in similar numbers of bacteria per phagocyte as that for aCF-Vibrio-FITC. **, statistically significant; ns, not significant.