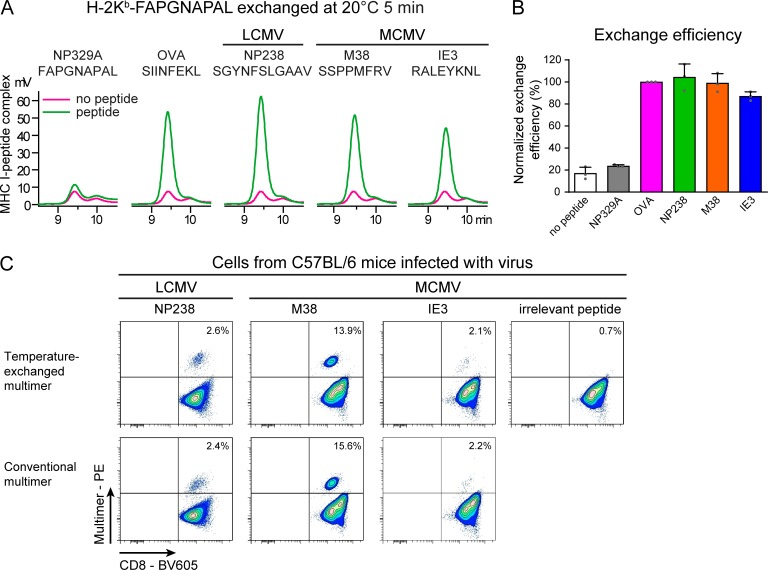
Figure 3.
Temperature-exchanged H-2Kb multimers are suitable for staining antigen-specific T cells from virus-infected mice. (A–C) H-2Kb–FAPGNAPAL monomers (A and B) or multimers (C) were exchanged for FAPGNAPAL (Sendai virus), SIINFEKL (OVA), SGYNFSLGAAV (LCMV NP238), SSPPMFRV (MCMV M38), or RALEYKNL (MCMV IE3) for 5 min at 20°C. (A) Primary data of temperature-induced peptide exchange on H-2Kb monomers analyzed by analytical gel filtration chromatography at room temperature. One of three representative experiments is shown. (B) Exchange efficiency calculated from the area under the curve from HPLC chromatograms normalized to the binding of optimal peptide (SIINFEKL). Mean values ± SD from three independent experiments (single data points depicted as gray dots) are shown. (C) H-2Kb–FAPGNAPAL multimers were exchanged for the indicated peptides and subsequently used to stain corresponding CD8+ T cells in PBMCs of an LCMV-infected mouse or splenocytes from an MCMV-infected mouse. Percentages of CD8+ T cells detected by flow cytometry were comparable between temperature-exchanged multimers and conventional multimers. Irrelevant peptide: FAPGNYPAL (Sendai virus). One of two representative experiments is shown. Multimer+ CD8+ T cells are indicated as percentage of total CD8+ cells. Cells were gated as described in Fig. S4 B.