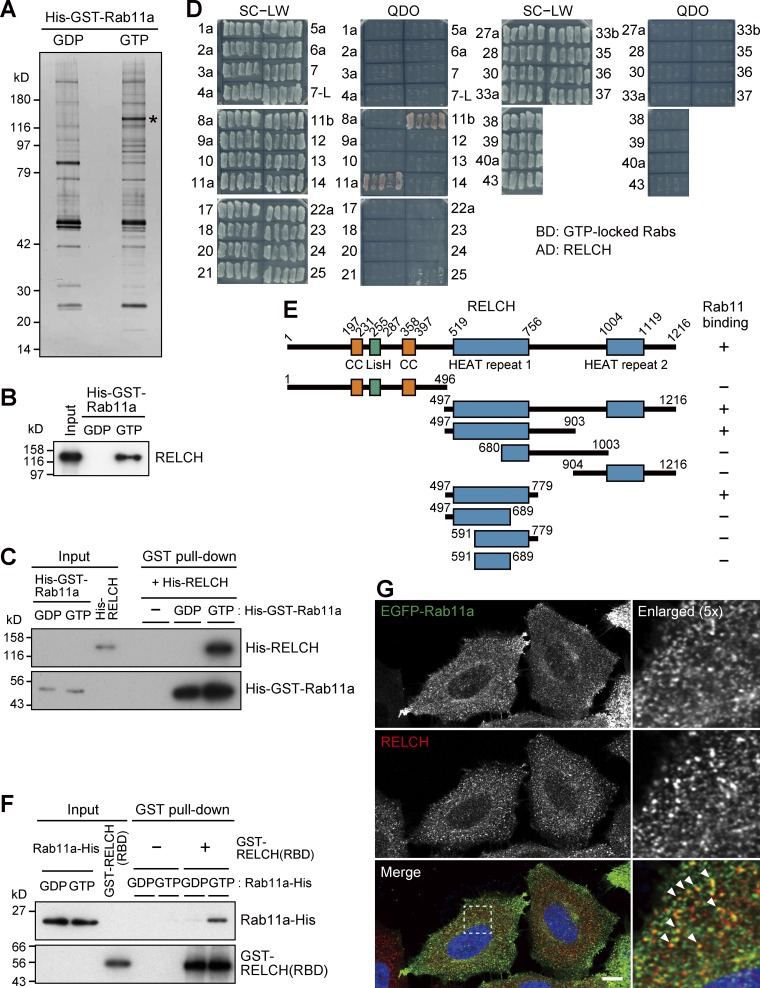
Figure 1.
Identification of RELCH as a Rab11-interacting protein. (A) The bead-bound GST-Rab11a WT or Q70A protein was incubated with a mouse brain lysate and GDP or GTP, respectively. The samples were separated on 4–12% gradient gels and silver-stained. The band with the asterisk was analyzed by performing mass spectrometry. (B) The pulled-down samples shown in A were immunoblotted with a RELCH antibody. (C) In vitro pulldown assay using purified recombinant RELCH and GST-Rab11-GTP or -GDP. The samples were immunoblotted with RELCH and GST antibodies. (D) Yeast two-hybrid assay using RELCH and GTP-locked Rabs. Yeast cotransformed with Gal4AD (AD) and Gal4BD (BD) plasmids encoding RELCH and Rab-GTP, respectively, was grown on SC−LW plates. Five independent colonies were selected and restreaked on SC−LW and QDO plates. Growth on the QDO plate indicates an interaction between the two proteins. (E) The interaction between Rab11 (Q70A) and a series of RELCH deletion mutants was tested by performing a yeast two-hybrid assay. The original data are shown in Fig. S1 A. (F) In vitro binding assay using the GST-tagged RBD of RELCH (GST-RELCH [RBD]) and C-terminal His-tagged Rab11a S25N or Q70A loaded with GDP or GTP, respectively. The samples were immunoblotted using Rab11 and GST antibodies. (G) HeLa cells expressing EGFP-Rab11a were immunostained with the RELCH antibody. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The arrowheads indicate RELCH-positive structures overlapped with EGFP-Rab11a–positive structures. Bar, 10 µm.