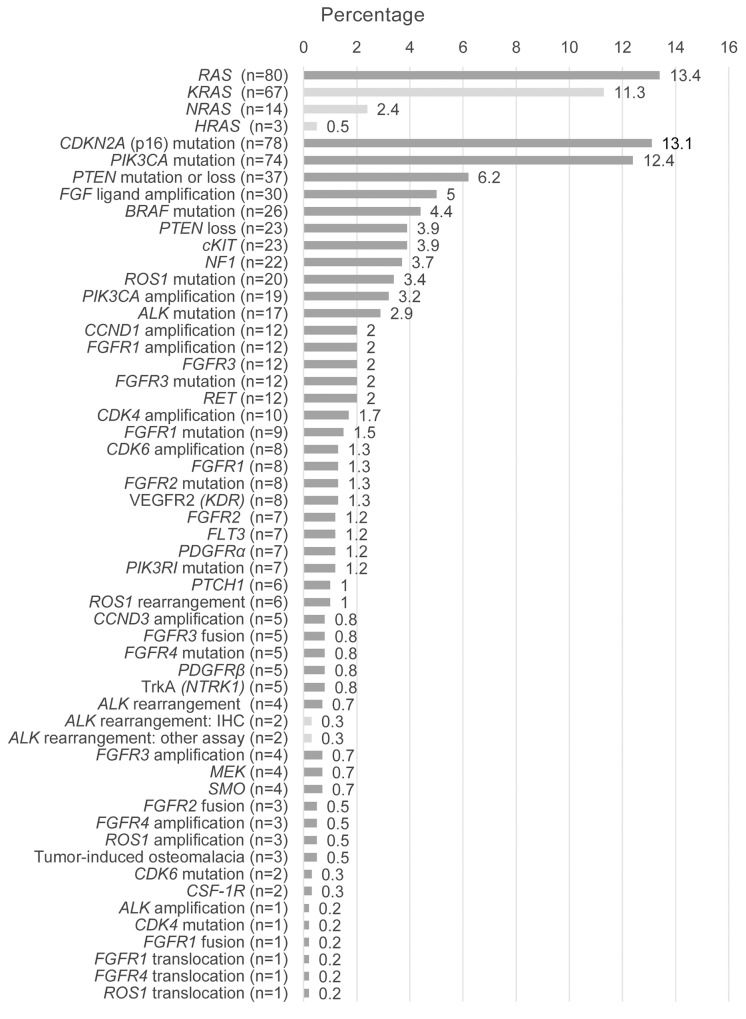
Figure 2. Summary of local alteration types (N = 595).
ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; CCND, cyclin D; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; CDKN2A, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; CSF-1R, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; FLT3, fms-related tyrosine kinase 3; HRAS, Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; IHC, immunohistochemistry; KDR, kinase insert domain receptor; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal–regulated kinase kinase; NF1, neurofibromatosis type 1; NRAS, neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog; NTRK1, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit α; PIK3RI, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit polypeptide 1; PTCH1, patched 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; SMO, smoothened; TrkA, tropomyosin receptor kinase A; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor. aPatients may have been counted in > 1 category; bPTEN loss determined by IHC (< 10% of tumor cells expressing PTEN at 1+ level); cReferring to ALK positivity.