Scheme 2.
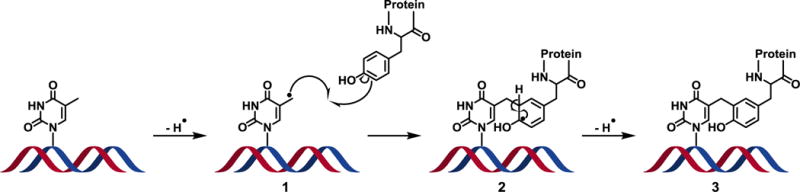
Proposed mechanism of hydroxyl radical-induced DPC formation between thymidine in DNA and tyrosine residue in proteins. Hydroxyl radicals abstract a hydrogen from the 5-methyl position of thymidine to yield a reactive thymidine radical (1), which undergoes a one-electron addition to the 3-position of a tyrosine to yield a stable methylene linkage. Subsequent hydrogen abstraction from the 3-position of tyrosine (2) rearomatizes the phenol ring to yield the stable DNA-protein cross-link (3).
