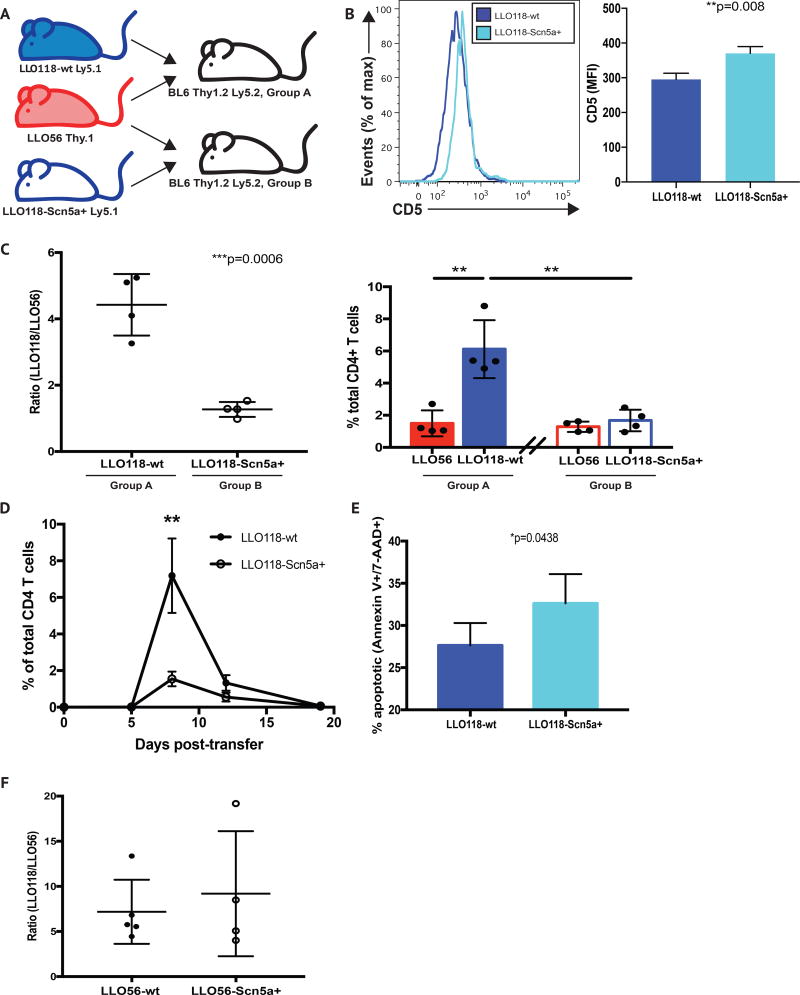
Figure 4. CD4+ T cells expressing the self-sensitizing Scn5a channel have an impaired response to Listeria monocytogenes infection.
(A) Recipient B6 (CD45.2+ and CD90.2+) mice were co-injected with either 104 LLO56 CD90.1+ T cells and 104 LLO118 CD45.1+ T cells (Group A), or 104 LLO56 CD90.1+ T cells and 104 Scn5a-expressing LLO118 CD45.1+ T cells (Group B), on day 0. (B) Within the CD3+CD4+ T cell compartment of wt and Scn5a-expressing LLO118 naive mice, CD5 levels were analyzed and compared, using mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (C) Mice from Groups A and B were IV injected with 103 CFU L. monocytogenes in PBS on day 1, and mice were sacrificed at day 7. Red blood cell-lysed, single cell splenocyte suspensions from both groups were analyzed by FACS. Live dead/gating was followed by doublet discrimination. CD3+CD4+ cells were then analyzed for the presence of CD45.1+ (LLO118) and CD90.1+ (LLO56) donor cells, and the resulting ratios (left) and absolute percentages (right) of these populations are shown. Data are representative of three separate experiments, with a minimum of 4 mice per group, per experiment. (D) A time course analysis of cell expansion was performed using the same experimental setup described in (C). A minimum of 3 mice from each cohort was analyzed at days 4, 7, 12 and 19 post-infection. (E) Ly5.1-marked cells recovered from donors receiving either wt LLO118 or Scn5a+ LLO118 cells CD4+ T cells were analyzed for the presence of apoptosis at day 7 post-infection, via Annexin V and 7-AAD staining. (F) Recipient B6 (CD45.2+ and CD90.2+) mice were co-injected with either 104 LLO56 CD90.1+ T cells and 104 LLO118 CD45.1+ T cells, or 104 Scn5a-expressing LLO56 CD90.1+ T cells and 104 LLO118 CD45.1+ T cells, on day 0. Both sets of receipients were IV injected with 103 CFU L. monocytogenes in PBS on day 1, and mice were sacrificed at day 7. Red blood cell-lysed, single cell splenocyte suspensions from both groups were analyzed by FACS. Live dead/gating was followed by doublet discrimination. CD3+CD4+ cells were then analyzed for the presence of CD45.1+ (LLO118) and CD90.1+ (LLO56) donor cells, and the resulting ratios are shown. Data are representative of three separate experiments, with a minimum of 4 mice per group, per experiment.