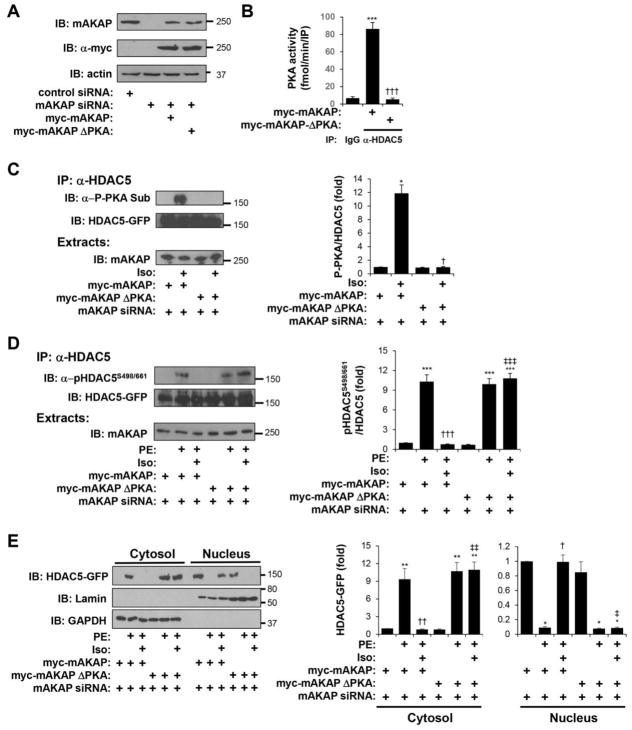
Figure 7. mAKAPβ-bound PKA is required for β-adrenergic-induced HDAC5 phosphorylation and inhibition of α-adrenergic-stimulated nuclear export.
Cardiac myocytes transfected with either mAKAP-specific or control siRNA were infected with adenovirus expressing myc-tagged wildtype mAKAP or a full-length PKA binding site mutant (ΔPKA) lacking residues 2053–2073 [24]. A. Western blot showing endogenous and myc-tagged mAKAP protein expression confirming RNAi-rescue. B. PKA activity assays were performed following immunoprecipitation with HDAC5 antibodies or control IgG. * vs. IgG; † vs. myc-mAKAP. C. Myocytes were treated for 10 min with 10 μM Iso. HDAC5-GFP immunoprecipitated with a HDAC5 antibody was detected using a PKA phospho-substrate-specific antibody that detects phosphorylated Ser-279 [13]. * vs. no drug; † vs. myc-mAKAP. D. Myocytes were stimulated with 10 μM Iso for 10 min followed by 50 μM PE for 1 hr. HDAC5-GFP was immunoprecipitated with a HDAC5 antibody and detected using a phospho-specific antibody for Ser-498/661. E. Cytosolic and nuclear extracts were prepared from myocytes treated as in D and analyzed by western blotting with HDAC5, lamin (nuclear marker), or GAPDH (cytosolic marker) antibodies. For D and E: Data are normalized to that for control peptide without Iso or PE. * vs. no drug; † vs. PE; ‡ vs. myc-mAKAP with PE and Iso. n = 3 for each panel.