Figure 10.
Dense network of acetylcholine esterase positive nerves immediately below the splenic capsule.
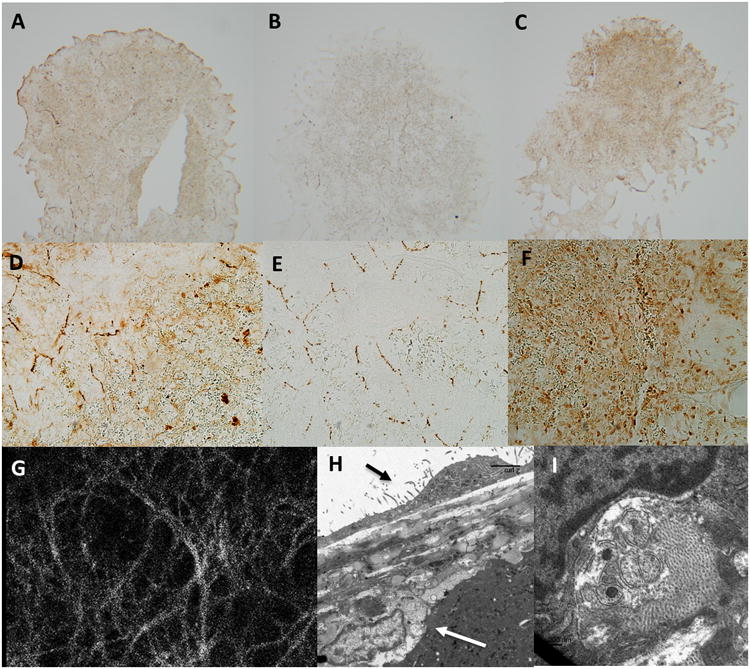
Panel a and d; Thin (5mm) sections through the frontal plane of the splenic capsule indicate strong and diffuse positive staining for the pan neuronal marker PGP9.5 in the capsular layer. Panel a, original magnification 5×. Panel d, original magnification 20×.
Panel b and e; Thin (5mm) sections through the frontal plane of the splenic capsule indicate strong positive staining for the sympathetic neuronal marker tyrosine hydroxylase in the capsular layer with tyrosine hydroxylase positive tissue forming a lose web of interconnected nerves. Panel b, original magnification 5×. Panel e, original magnification 20×.
Panel c and f; Thin (5mm) sections through the frontal plane of the splenic capsule indicate strong and diffuse positive staining for the para-sympathetic neuronal marker acetylcholine esterase in the capsular layer. Panel c, original magnification 5×. Panel f, original magnification 20×.
Panel g; The splenic capsule viewed at 40X on a confocal microscope. Tissue was loaded with the Ca2+ sensitive indicator fluo-4. Note a dense layer of nerve tissue can be observed directly below the mesothelial cell layer across the entire splenic capsule. The density of this neural web is much greater than that observed in panel b and e in tissue stained positive for tyrosine hydroxylase, indicating additional nerve tissue is present. Activation of these nerves can be stimulated by electrical field stimulation (see supplement)
Panel h; Transmission electron microscopy indicates that nerves sit directly below the splenic capsule. Black arrow indicates capsular mesothelial cell. White arrow indicates nerve closely associated with the splenic capsule. Bar=5μm.
Panel i; Nerves are identified by the presence intracellular vesicles typical of synaptic junctions.
