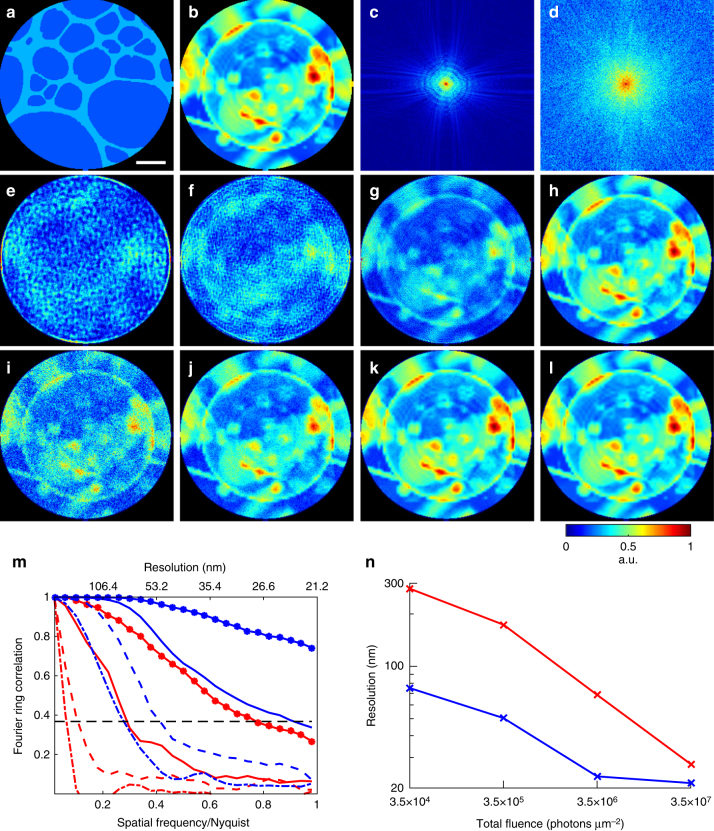
Fig. 5.
Numerical simulations of potential significant dose reduction using in situ CDI. a A simulated 20-nm-thick Au pattern in 1-µm-thick H2O static structure. The diameter of the pinhole is 3 µm. b A simulated biological sample of a vesicle and protein aggregates in 1-µm-thick H2O. c Soft X-ray diffraction pattern with a 5 × 5 missing center, calculated from the biological sample with a photon energy of 530 eV and a fluence of 3.5 × 107 photons µm−2. Poisson noise was added to the diffraction intensity. d Soft X-ray diffraction pattern calculated from the biological sample with a fluence of 3.5 × 107 photons µm−2 and the static structure with a fluence of 1.4 × 1010 photons µm−2. Poisson noise was added to the diffraction intensity. The center-to-center distance between the biological sample and static structure is 3.8 µm. e–h Image reconstructions of the biological sample without the static structure, with fluences 3.5 × 104, 3.5 × 105, 3.5 × 106, and 3.5 × 107 photons µm−2, respectively. i–l Image reconstructions with the same fluences on the biological sample as e–h, but with additional 1.4 × 1010 photons µm−2 on the static structure. m Fourier ring correlation of the reconstructions and the model. Red lines correspond to e–h (dash-dot, dashed, solid, solid-dotted lines, respectively), and blue lines to i–l. n Achieved spatial resolution of each reconstruction determined by the 1/e threshold in the Fourier ring correlation. Scale bar, 400 nm