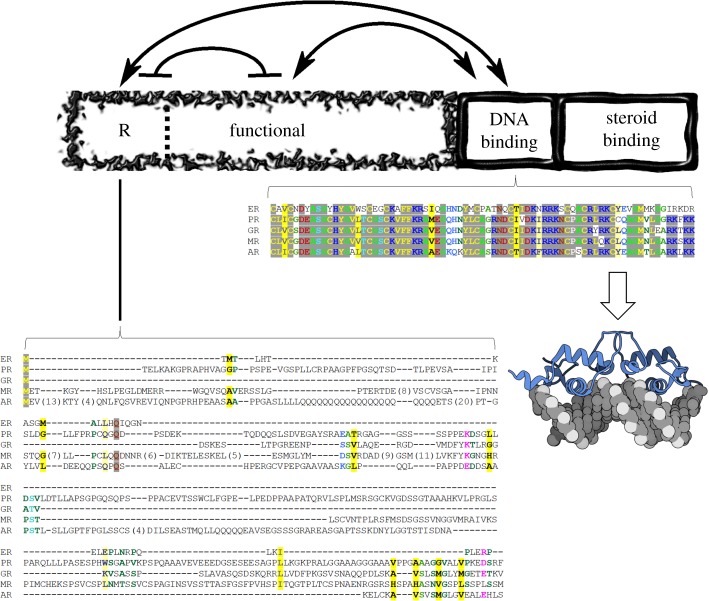
Figure 1.
Domain architecture of glucocorticoid receptor and sequence conservation within the human steroid hormone receptor family. The domains are depicted as boxes relative to their amino-acid lengths. The DNA-binding and steroid-binding domains are dynamic and shown as wavy boxes. The N-terminal domains, regulatory (R) and functional (F), are intrinsically disordered and shown as a fragmented box that makes up the N-terminus. Thermodynamic interactions are shown as lines with arrows (stabilizing interaction) or with bars (destabilizing interaction) [18,19]. Amino-acid sequence conservation of DBD, the most conserved region of the family, and conservation of the R-domain (residues 1–97), the least conserved region, are explicitly shown [23]. Stronger colour density indicates a higher degree of conservation, yellow denotes hydrophobic side chains, red/blue indicates charged and polar side chains [24]. ER, Estrogen Receptor; PR, Progesterone Receptor; GR, Glucocorticoid Receptor; MR, Mineralocorticoid Receptor; AR, Androgen Receptor. The cartoon molecule denotes the Protein Data Bank structure of GR DBD bound to PAL DNA, accession number 3g99.