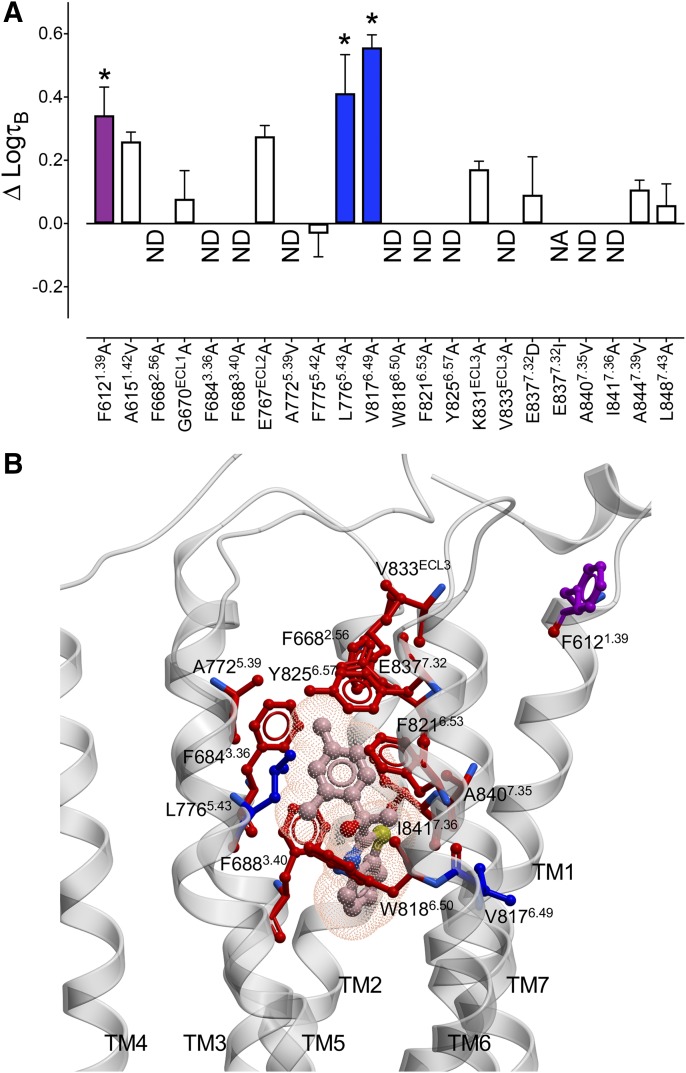
Fig. 5.
7TM and ECL mutations alter AC265347 efficacy at the CaSR. (A) Previously published concentration-response curves to Ca2+o in the absence and presence of AC265347 determined in Ca2+i mobilization assays (Leach et al., 2016) were reanalyzed with an operational model of allosterism that accounted for ambient divalent cations (eq. 1) to determine the change in AC265347 efficacy (ΔτB) at the mutant CaSRs in comparison with the WT receptor. White bars represent no significant change in τB. Colored bars that sit above zero represent an increase in τB. A significant 1.6–2.5-fold increase in τB is represented by the purple bar and a greater than 2.5-fold increase is represented by blue bars. ND, not determined due to negligible efficacy; NA, no PAM activity. Data are the ΔτB + S.E.M. calculated from WT and mutant τB values and experiment numbers shown in Table 2; * demotes significant difference in comparison with WT (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test). Efficacy residues are shown on a CaSR 7TM domain homology model (B), along with the predicted AC265347 pose from docking studies. Blue and purple colors correspond to the fold change in efficacy shown in (A), whereas red corresponds to a complete loss in AC265347 efficacy.