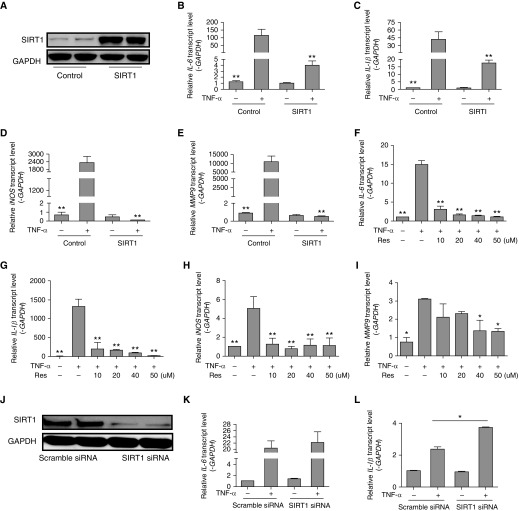
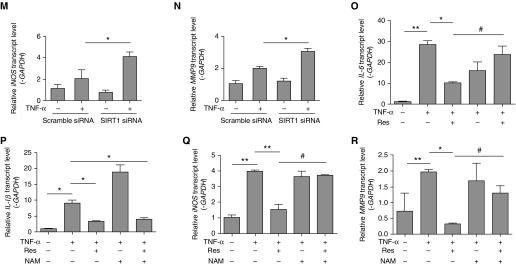
Figure 3.
SIRT1 inhibits inflammation induced by TNF-α. (A) MRC-5 human fetal lung fibroblasts were transiently transfected with SIRT1 plasmid or control plasmid and whole-cell lysates were used for immunoblotting of SIRT1. (B–E) MRC-5 cells were transiently transfected with control or SIRT1 plasmid for 6 hours, then incubated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for another 6 hours, and transcript abundance was quantified. (F–I) Cells were stimulated with TNF-α in the absence or presence of Res (0, 10, 20, 40, or 50 μM) for 6 hours, and transcript abundance was quantified. (J) Cells were transfected with control silence RNA (siRNA) or SIRT1 siRNA, and whole-cell lysates were used for immunoblotting of SIRT1. (K–N) Cells were transiently transfected with siRNA for 6 hours, then incubated with exogenous TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for another 6 hours, and transcript levels were evaluated. (O–R) Cells were treated with vehicle or 20 mM nicotinamide (NAM) for 6 hours, and then exposed to 10 ng/ml TNF-α with or without added 50 μM Res for another 6 hours. RT-PCR was used to quantify the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, iNOS, and MMP9 mRNA. The mRNA levels were calculated using a relative ratio to GAPDH. Mean (±SEM), n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 versus cell exposure to TNF-α only. (O–R) #P < 0.05 versus cell exposure to NAM. Findings were confirmed in three separate experiments.