Fig. 1.
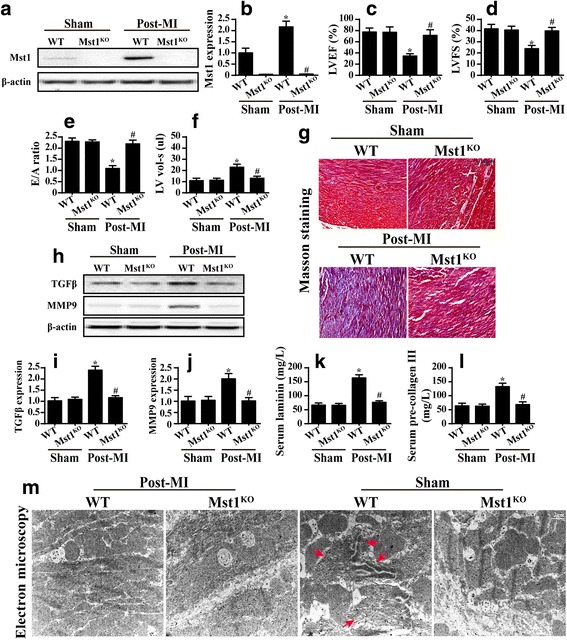
Mst1 levels were higher in the myocardium after a myocardial infarction (MI) and this contributed to the chronic cardiac damage. a and b The expression of Mst1 in the post-MI myocardium (Post-MI) in wild-type (WT) and Mst1-knockout (Mst1KO) cells relative to the control (Sham). c–f The cardiac function was detected as LVEF, LVFS, E/A ratio and LV vol-s via echocardiography in WT and Mst1KO cells. g Masson staining was used to observe cardiac fibrosis. h–j The signaling pathways related to cardiac fibrosis (TGFβ and MMP9) were assessed via western blotting in WT and Mst1KO cells. k and l The serum laminin and precollagen III levels in WT and Mst1KO cells were measured via ELISA. m Electron microscope observations of the ultra-structural alterations in WT and Mst1KO mice after MI. Red arrows indicated Z-line disappearance, cardiac muscle dissolution and cardiomyocyte disorganization. *p < 0.05 vs. sham group, #p < 0.05 vs. WT mice in post-MI group
