Fig. 2.
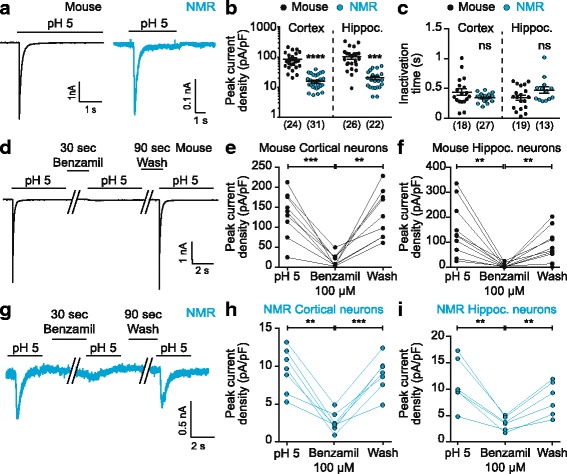
ASICs mediate acid-induced currents in NMR and mouse CNS neurons. a Both mouse (black trace, left) and NMR (blue trace, right) neurons respond to a pH 5 solution with a transient inward current. b Acid-induced currents are of significantly smaller amplitude in NMR neurons compared to mouse neurons. c Inactivation time constants of the acid-induced responses are similar between NMR and mouse neurons. d Example trace of an acid-induced current elicited by a pH 5 solution and the effect of 100 μM benzamil in a mouse cortical neuron. e, f Acid-induced currents in both cortical and hippocampal mouse neurons were reversibly blocked by 100 μM benzamil (n = 9 and n = 10 cortical and hippocampal neurons, respectively). g Example trace of an acid-induced current evoked by a pH 5 solution in a cortical NMR neuron showing inhibition by 100 μM benzamil. h, i In both cortical (n = 7) and hippocampal (n = 6) NMR neurons, acid-induced currents were reversibly blocked by 100 μM benzamil. ** p < 0.01; **** p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA paired tests, Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. Numbers into brackets indicates the number of recorded cells
