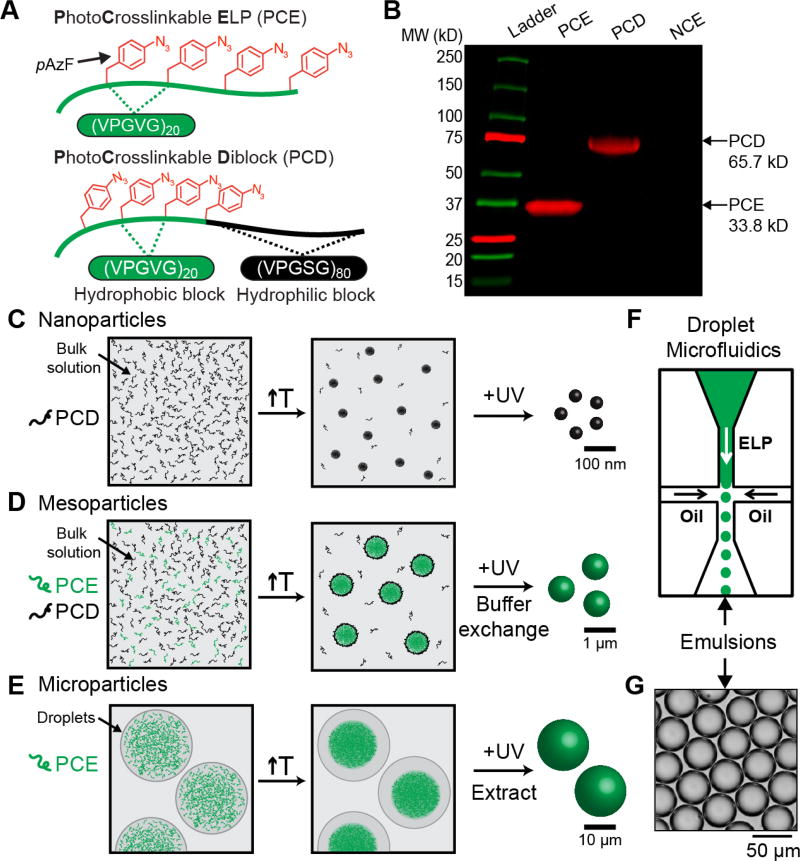
Figure 1. Design of size-controlled, thermoresponsive gel particles composed of disordered polypeptides containing photocrosslinkable unnatural amino acids.
(A) Schematic of the two disordered polypeptides used in this study — photocrosslinkable ELP (PCE) and photocrosslinkable diblock (PCD). (B) Fluorescent SDS-PAGE gel of PCE, PCD, and NCE (non-crosslinkable ELP, (VPGVG)80) labeled with DBCO-Cy5. PCE and PCD contain pAzF residues which react with DBCO-Cy5, while the negative control NCE is not fluorescently labeled via click. (C) Strategy for generating nanoparticles by heating and crosslinking PCD in bulk solution. (D) Strategy for generating mesoparticles by heating and crosslinking mixtures of PCE and PCD in bulk solution. The PCD acts as a surfactant to stabilize PCE particles after heating, and buffer exchanging removes free PCD following crosslinking. Mesoscale particles can also be generated in microfluidic droplets for fluorescent spatial tracking. (E) Strategy for generating microparticles by heating and crosslinking solutions of PCE in microfluidic droplets, followed by particle extraction from droplets. (F) Schematic of a chip-based microfluidic droplet generator for generating monodisperse ELP-containing water droplet templates. (G) Brightfield images of monodisperse water droplets containing photocrosslinkable ELPs.