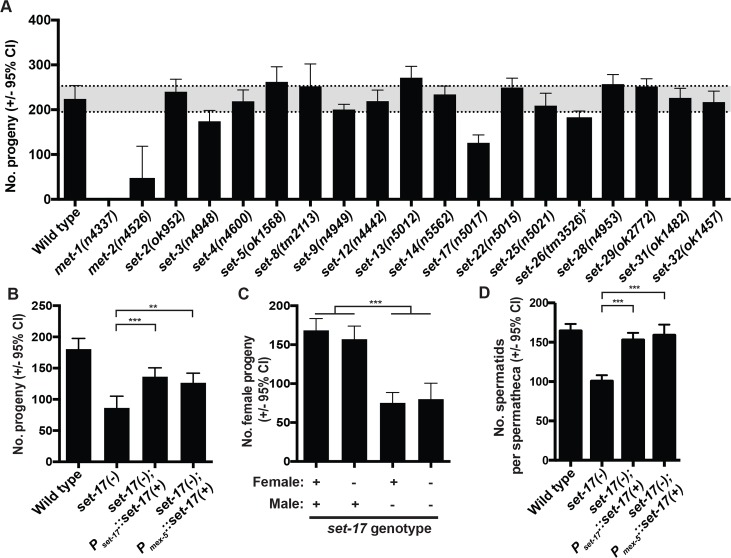
Fig 3. set-17 functions in the germline to promote sperm-production and fertility.
A) Broodsizes of mutants defective in KMT genes expressed in the germline. Progeny number was determined for single adult hermaphrodites over three days and progeny were scored as adults after 3–6 days. Grey shaded area indicates the range of the wild-type 95% confidence interval. n > 10 for all genotypes. set-23, set-24 and set-27 mutants were not available, and instead these genes were examined using RNAi treated wild-type animals; fertility was not affected. B) Broodsize of wild-type, set-17, set-17; Pset-17::set-17(+) (expressing wild-type set-17 from its endogenous promoter) and set-17; Pmex-5::set-17(+) (expressing wild-type set-17 from the mex-5 germline-specific promoter) hermaphrodites. n > 20; *** P < 0.0001, ** P < 0.0012, t-test. C) Progeny of mating single males (wild-type or set-17 mutant) and single females (wild-type or set-17 mutant). Strains carried the fog-2(q71) mutation, which feminizes hermaphrodites by suppressing hermaphrodite but not male sperm production and ensured that all progeny were cross progeny. After 24 hr the male was removed, and the female allowed to lay progeny until completion. Females were placed on fresh plates every 24 hr over 4 days. Cross progeny were scored as number of adult female progeny 3–7 days after mating; only females were scored because adult males burrow, crawl off plates and clump together, making their quantification unreliable. n > 15. *** P < 0.0001, t-test. D) Spermatid counts in individual spermathecas of the indicated genotypes. Spermatid counts were determined by imaging DAPI-stained spermatid nuclei in hermaphrodites fixed in 4% formaldehyde 12 hr post-L4 around the time of first fertilization. n: wild-type = 26, set-17(-) = 32, set-17(-); Pset-17::set-17(+) = 33, set-17(-); Pmex-5::set-17(+) = 15. *** P < 0.0001, t-test.