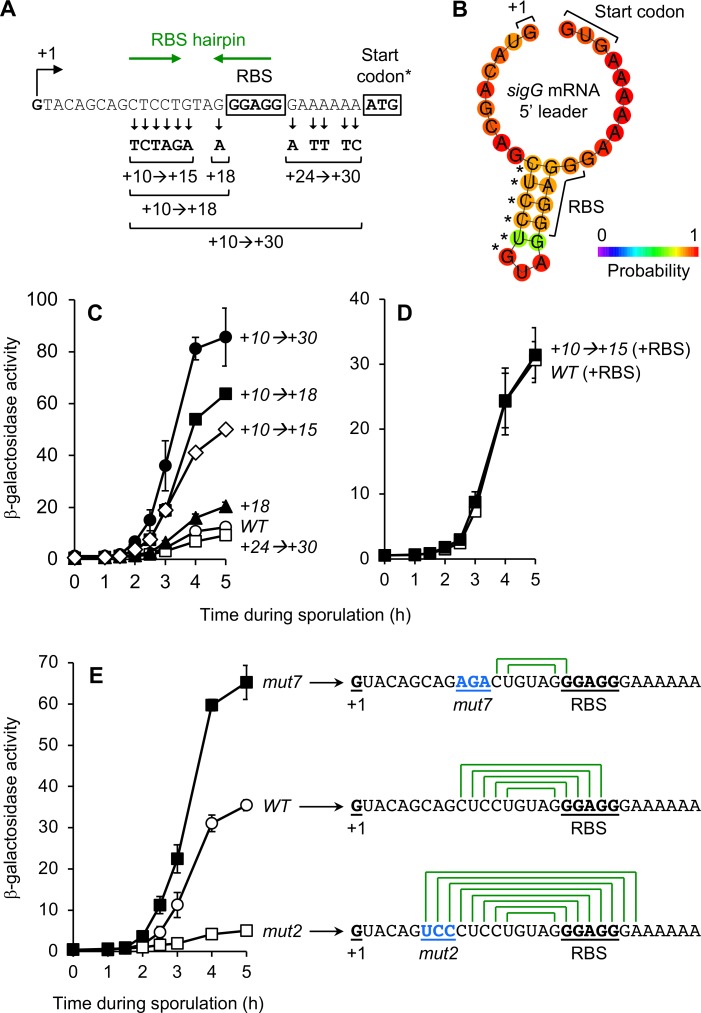
Fig 5. An mRNA hairpin formed between the sigG leader sequence and RBS significantly decreases PsigG-lacZ translation.
(A) Depiction of the mutations in the PsigG+10→+30-lacZ reporter variant, as well as variants designed to harbor only a subset of these mutations. The sigG transcription start site (+1), sigG ribosome-binding site (RBS), and ATG start codon are indicated. (*Note that the PsigG-lacZ reporter gene used here harbored the non-native ATG start codon in place of the native sigG GTG start codon.) Also indicated, with green arrows, are complementary sequences predicted to form the RBS hairpin structure shown in (B). (B) Depiction of the sigG RBS-hairpin structure predicted to form in the sigG mRNA leader sequence. The 5’ end of the sigG mRNA (+1), the sigG core RBS, and native GTG (GUG) translation start codon are labeled. Asterisks indicate the six nucleotide positions altered in the +10→+15 mutant. The prediction and graphic were generated by ViennaRNA, with bases color-coded according to their partition function probabilities [68]. (C) Alteration to nucleotides upstream of the sigG RBS stimulates expression from a PsigG-lacZ reporter gene. The activities of PsigG+10→+30-lacZ (+10→+30; closed circles), PsigG+24→+30-lacZ (+24→+30; open squares), PsigG+10→+18-lacZ (+10→+18; closed squares), PsigG+18-lacZ (+18; closed triangles), PsigG+10→+15-lacZ (+10→+15; open diamonds), and the corresponding wild type PsigG-lacZ (WT; open circles) were measured during sporulation. (Strains AHB883, AHB2124, AHB2126, JC68, JC70, and AHB1274, respectively.) (D) The +10→+15 alterations do not impact β-galactosidase production from a transcriptional lacZ reporter. β-Galactosidase production was monitored during sporulation of strains harboring PsigG-RBS-lacZ (WT [+RBS]; open squares) and PsigG+10→+15-RBS-lacZ (+10→+15 [+RBS]; closed squares). (Strains AM3 and AM4, respectively.) In these transcriptional reporters, lacZ is separated from the sigG RBS by a spacer and provided with an engineered RBS. (E) Mutations that weaken/eliminate or strengthen the sigG RBS-hairpin increase or decrease PsigG-lacZ expression, respectively. The activities of PsigGmut7-lacZ (mut7; closed squares), PsigGmut2-lacZ (mut2; open squares), and the corresponding wild type PsigG-lacZ (WT; open circles) were measured during sporulation. (Strains JJB55, JJB37, and JJB31, respectively.) The mRNA leader sequence for each PsigG-lacZ variant is indicated to the right, with the 5’ end of the mRNA (+1), core RBS, and the mut7 or mut2 mutations (in blue) labeled and underlined. Also depicted is the capacity for formation of a hairpin structure (green lines connecting complementary base-pairs). For all relevant panels, error bars indicate ± standard deviations based on three independent experiments.