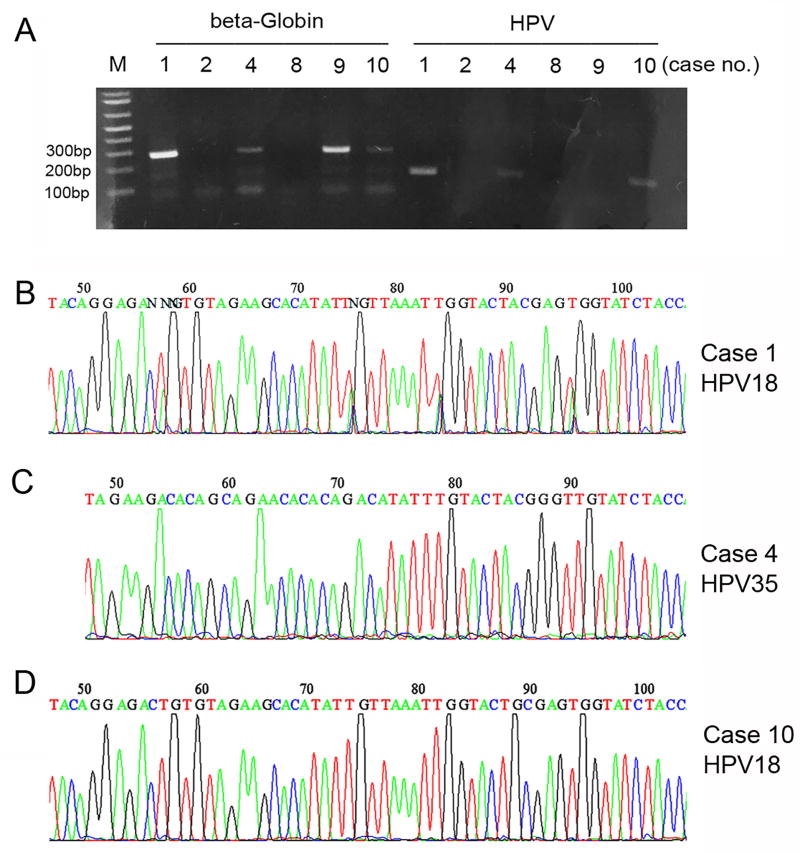
Figure 2.
PCR-based detection and typing of HPV. Case 1 with ISH-detected HPV 18 was used as positive control (A, B). The samples (cases 2, 4, 8, 9, 10) with no detectable high-risk HPV by ISH were checked for DNA integrity by amplifying β-globin as a housekeeping gene (A). The DNA samples (cases 4, 9, 10) with positive test results for β-globin were subsequently studied by nested PCR using MY09/MY11 and GP05/GP06 primers. The PCR products (A) were subjected to direct DNA Sanger sequencing to analyze the HPV type. Case 4 with HPV 35 (C); case 10 with HPV 18 (D); case 9 with no PCR-detectable HPV (A).