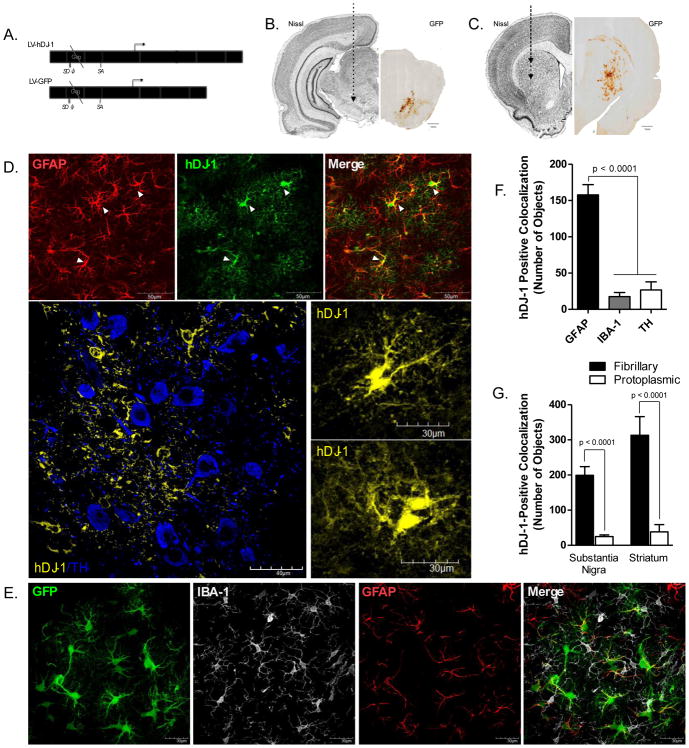
Figure 1. LV-hDJ-1/MuLV is expressed in astrocytes within the substantia nigra and striatum.
A. The Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (MuLV) protein coat encapsulates a lentiviral expression vector driving bicistronic expression of human DJ-1 (CMV promoter) and green fluorescent protein (GFP; iRES promoter) enabling GFP localization to distinguish cells co-expressing human DJ-1 protein. B–C. Stereotaxic targets within the striatum and substantia nigra (SN) of adult male Lewis rats were selected as the areas most affected by dopamine neuron cell body and terminal loss following rotenone treatment. D. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) marker for astrocytes (red) is colocalized with human DJ-1 (hDJ-1) overexpression (green) following LV-hDJ-1/MuLV expression vector transfection in the SN (100×). hDJ-1 immunoreactivity within the SN (60×) reveals hDJ-1 expression within astrocytic processes and cell bodies (hDJ-1, yellow) adjacent to dopamine neurons (TH, blue) but does not colocalize with TH; inset images of astrocytes overexpressing hDJ-1 (100×). E. Striatal expression of MuLV vector GFP (green) indicates colocalization with GFAP (red), but is excluded from microglia (IBA-1, white). F. Quantification of total hDJ-1 protein within cell types of the substantia nigra N=5 (F2,18 = 49.64, p < 0.0001). G. hDJ-1 colocalizes with fibrillary (GFAP-positive) astrocytes more than protoplasmic (ALDH1L1-positive) astrocytes within both the substantia nigra and striatum; N=5 (F3,30 = 16.26, p < 0.0001). Statistical analysis; one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post-hoc test.