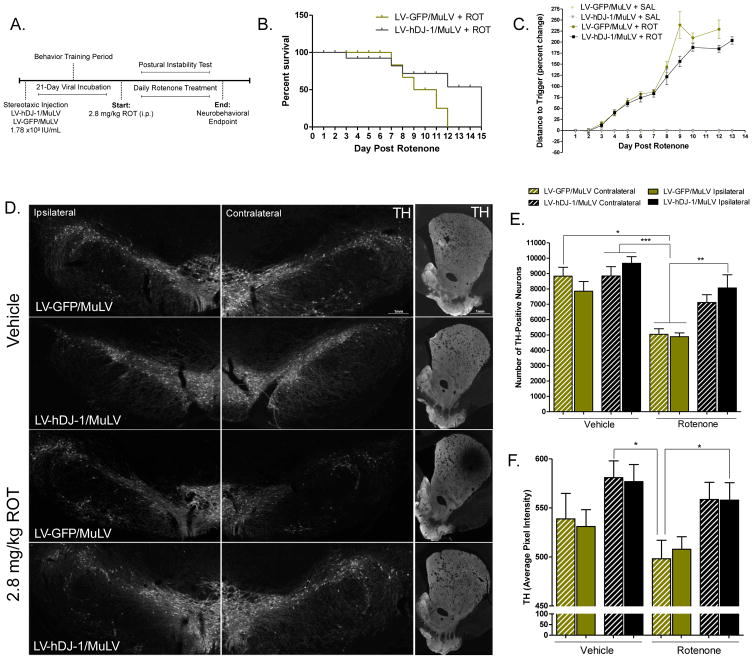
Figure 2. Overexpression of astrocytic hDJ-1 attenuates rotenone-induced neurotoxicity.
A. Dosing paradigm for MuLV injection followed by rotenone treatment. B. Animal survival following rotenone treatment in animals receiving hDJ-1 overexpression vector (MuLV-DJ-1) or GFP control vector (LV-GFP/MuLV); N=5 (χ2 = 2.104, p = .147), log-rank (Mantel-Cox) comparison of survival curves. C. Postural instability test (PIT) motor behavior scores during endpoint rotenone dosing paradigm; N=5 (p < 0.0001). Statistical analysis; Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. D. Representative montage images (20×) of SN and striatal tissue from LV-GFP/MuLV and MuLV-DJ-1 animals receiving saline or rotenone treatment. E. Stereological analysis of TH-positive neurons in the SN; N=5 (F7,26 = 9.61, p < 0.0001). F. Quantification of striatal TH intensity; N=5 (F3,382 = 21.44, p < 0.0001). Statistical analysis; one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post- hoc test (*p < 0.05, **p <0 .01, ***p < 0.001).