Fig.9.
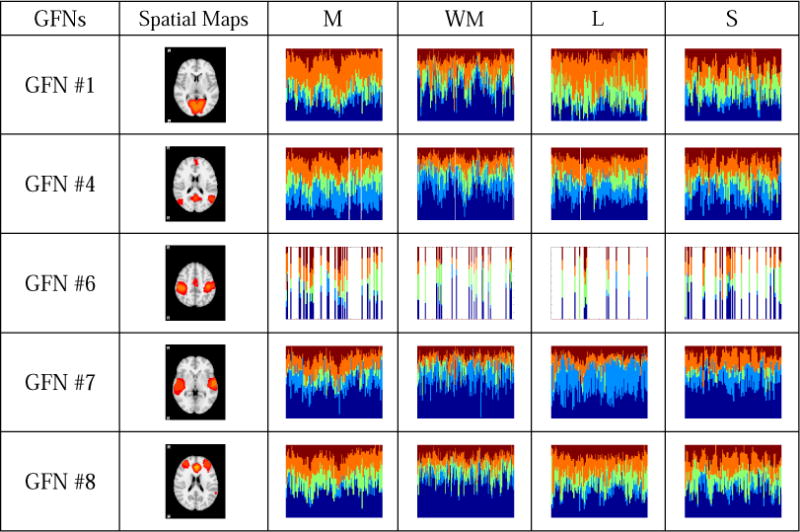
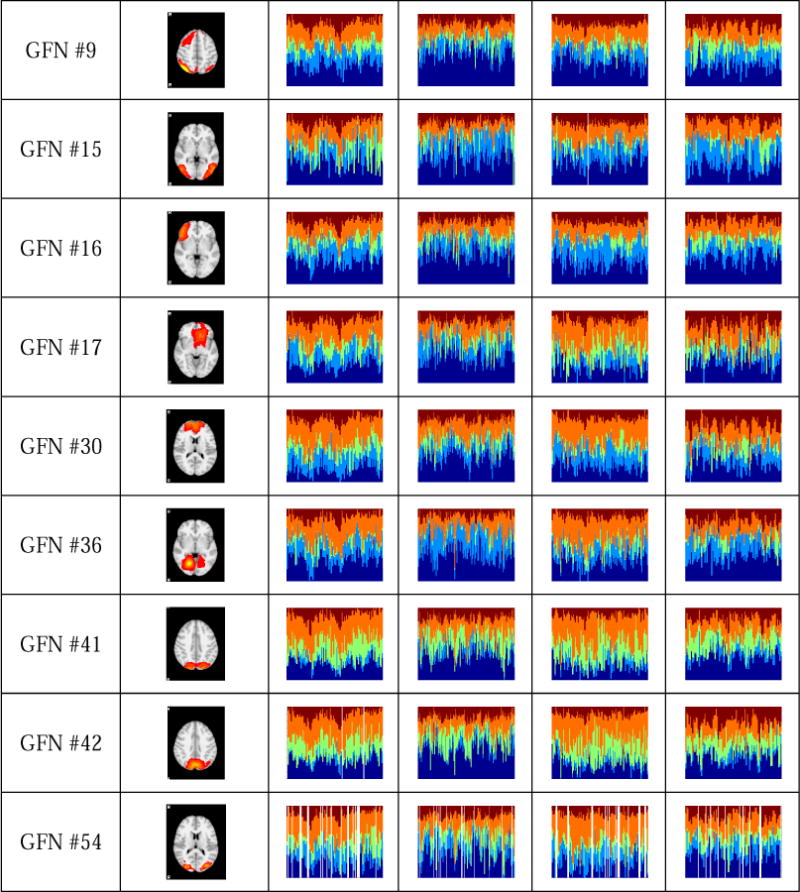
Fourteen GFNs which exhibit different behavioral patterns across four tasks. Each row presents time-evolving role mixed-memberships of four studied tasks of a GFN. The horizontal axis represents the time window (the layer of the time-evolving graph), while the vertical axis represents the role distribution in each time window. Five colors represent five different roles learned from the time-evolving graph model. The inactivity is represented by the white bars. According to interpretations on the roles in Fig.6, the role 1 represents the centrality of the time-evolving graph, which implies that the vertex in role 1 is the most influential in the graph. In contrast to the role 1, the role 2 represents that the vertex plays a less important role. The role 3 represents the bridge between other vertices of the graph. The roles 4 and 5 represent that the vertex has an important influence within a cluster, whereas it cannot serve as the global centrality of the whole graph.
