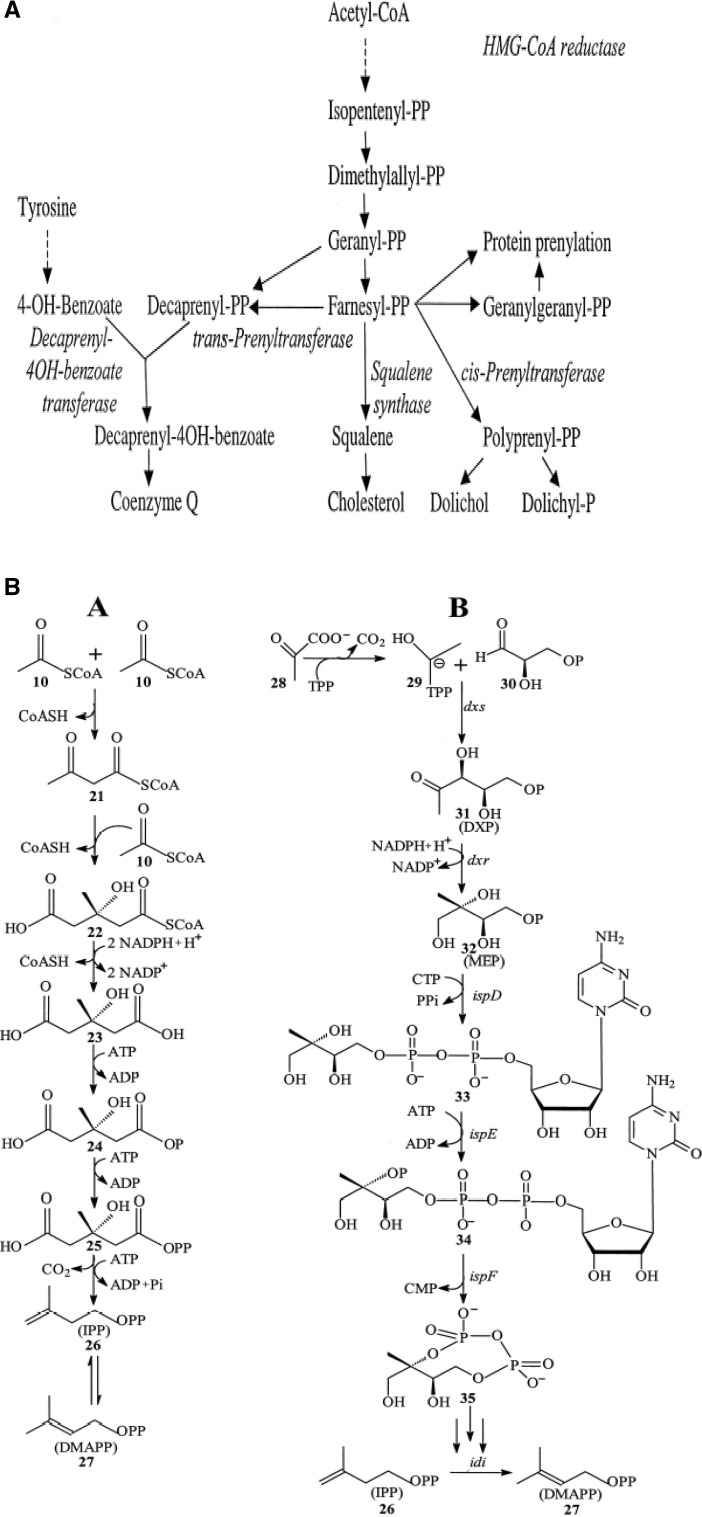
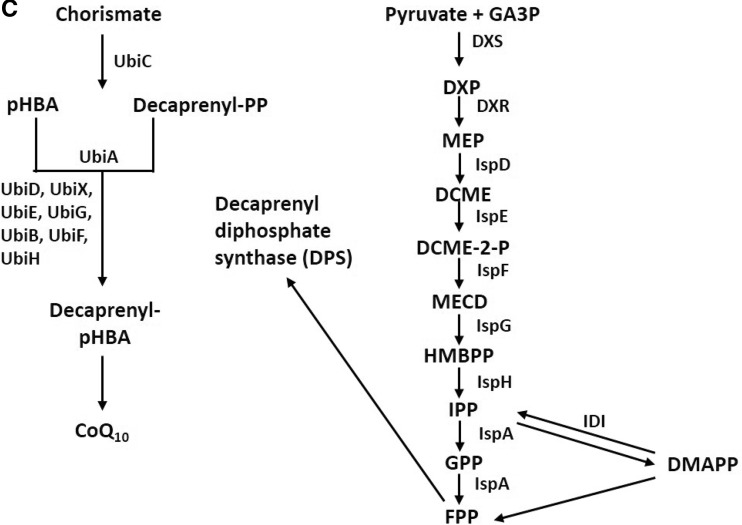
Fig. 5.
a Biosynthesis of coenzyme Q10 in eukaryote (Dallner and Sindelar 2000); b biosynthetic pathways for isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate synthesis (Meganathan 2001) A: Mevalonate pathway. 10, acetyl-CoA; 21, acetoacetyl-CoA; 22, HMG-CoA; 23, mevalonate; 24, mevalonate 5-phosphate; 25, mevalonate 5-diphosphate; 26, isopentenyl diphosphate; 27, dimethylallyl diphosphate. B: 2-C-Methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway. 28, pyruvate; 29, hydroxyethyl-TPP anion; 30, D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 31,1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP); 32, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP); 33, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol; 34, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2-phosphate; 35, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate; 26, isopentenyl diphosphate; 27, dimethylallyl diphosphate; c biosynthesis of coenzyme Q10 in prokaryotes (Jeya et al. 2010). Decaprenyl diphosphate synthesized by DPS combines with pHBA and undergoes a series of reactions for the production of CoQ10. 4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol (DCME) 2-phosphate, 2-Cmethyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MECD)