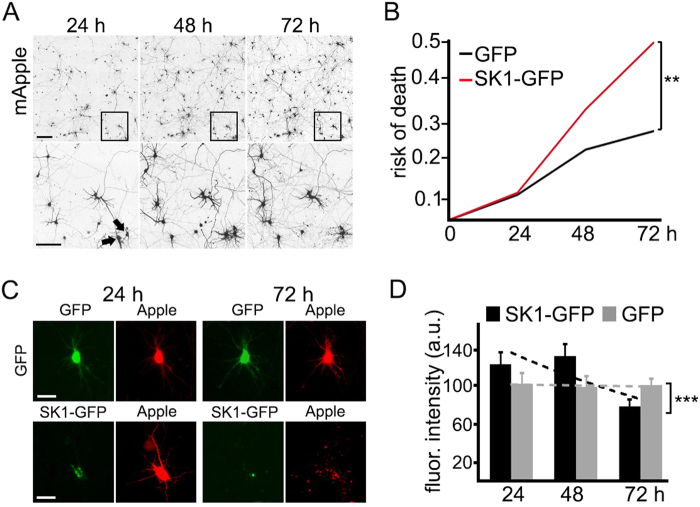
Fig. 4. Overexpressed SK1 is neurotoxic for primary cortical neurons.
a An example of survival analysis in neurons. Primary cortical neurons were transfected with mApple to visualize neuronal morphology. The same group of neurons was imaged 24 h after transfection and tracked over time with an automated microscope. Images collected after 24 h demonstrate the ability to return to the same field of neurons and to follow them over time. Each image in the top panels is a montage of non-overlapping images captured in one well of a 24-well plate at different time points (24, 48, and 72 h). Scale bar is 400 μm. In the bottom panel, a region from the original images is zoomed in to demonstrate longitudinal single-cell tracking. Black arrows depict two neurons that develop differently over time. The neurons on the left degenerate and disappear before 72 h after transfection, and the neuron on the right remains alive until the end of the experiment. Scale bar is 50 μm. b Primary cortical neurons were transfected with mApple and GFP or with mApple and SK1-GFP and tracked with an automated microscope for 72 h. Risk of death curves demonstrate that SK1-GFP expression is neurotoxic. **p (GFP vs SK1-GFP) = 0.0032 (log-rank test). Two hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments. c Primary cortical neurons were transfected with mApple and GFP or with mApple and SK1-GFP and imaged thereafter. Note that the SK1-expressing neuron died, while the control neuron was alive until the end of the experiment. Scale bar is 10 µm. d Primary neurons were transfected with mApple and GFP or with mApple and SK1-GFP. Neurons were imaged 24 h after transfection, and the green fluorescence intensity was measured in each neuron. To determine the dose-dependent toxicity in cortical primary neurons that express GFP or SK1-GFP, the green fluorescence intensities in individual neurons were correlated with the time at which each cell died. The bar graphs represent the correlate of average of GFP and SK1-GFP fluorescence intensities with neuronal longevity. Note that neuronal survival is not correlated with the expression of GFP. The graph bar contains the linear correlation slopes of GFP- and SK1-GFP-expressing neurons. The SK1-GFP fluorescence intensity of each neuron was correlated with the cell's risk of death. The SK1-GFP intensity is correlated with a higher risk of death. m (GFP) = −0.986; m (SK1-GFP) = −24.864. ***p = 0.0001 (t test). Two hundred neurons were analyzed from three independent experiments