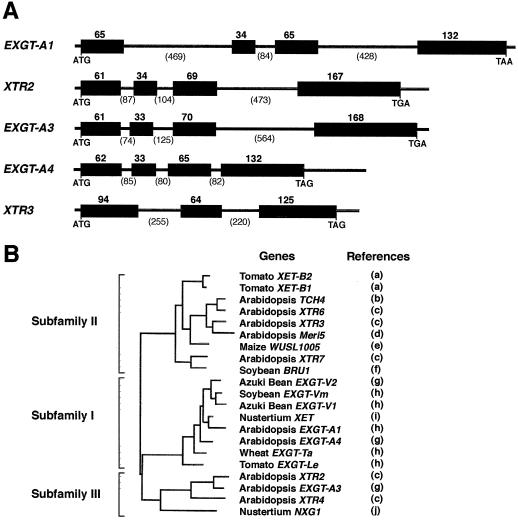
Figure 1.
Comparison of EXGT genes. A, Genomic structure of the EXGT genes cloned in this study. Protein coding regions are shown by black boxes with the number of amino acid residues encoded by each exon. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of nucleotides for intron. Intron splice sites in genomic sequences were deduced by comparison with their corresponding cDNA sequences, EXGT-A1 (Okazawa et al., 1993; accession no. D16454), XTR2 (Xu et al., 1996; accession no. U43487), EXGT-A3 (Nishitani, 1997; accession no. D63509), EXGT-A4 (Nishitani, 1997; accession no. AB026486), and XTR3 (Xu et al., 1996; accession no. U43485). The accession numbers for genomic sequences determined in this study are AF163819 (EXGT-A1), AF163820 (XTR2), AF163821 (EXGT-A3), AF163822 (EXGT-A4), and AF163823 (XTR3), respectively. B, Phylogenetic relationship between the Arabidopsis and other EXGT-related protein sequences. The entire deduced amino acid sequences were compared using the malign program of DNA Data Bank of Japan (Nishitani, 1997). References: a, Arrowsmith and de Silva (1995); b, Xu et al. (1995); c, Xu et al. (1996); d, Medford et al. (1991); e, Saab and Sachs (1995); f, Zurek and Clouse (1994); g, Nishitani (1997); h, Okazawa et al. (1993); i, Rose et al. (1996); and j, de Silva et al. (1993).