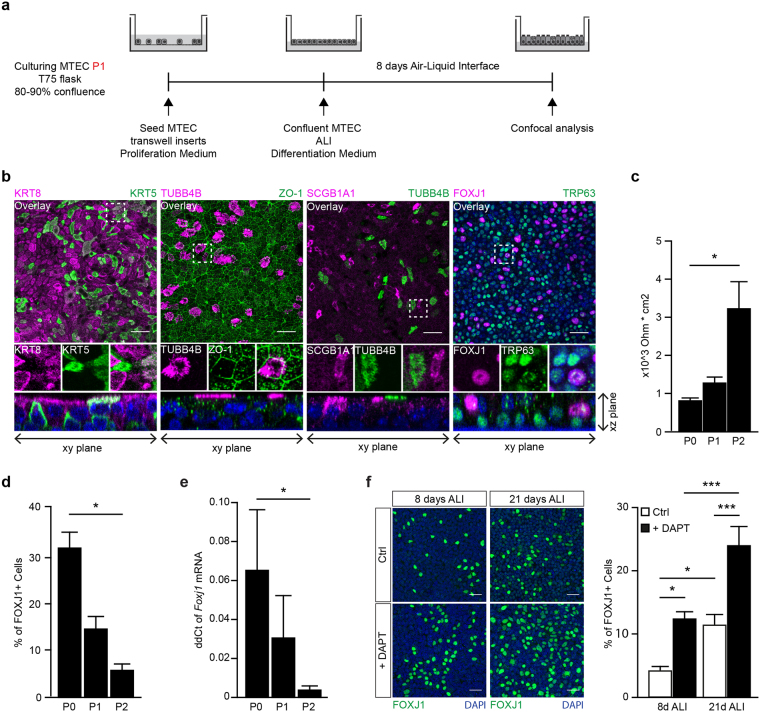
Figure 2.
Expansion of MTEC in vitro leads to decreased ciliary and club cell differentiation. (a) Schematic representation of culture protocol. (b) Co-staining of different epithelial markers on MTEC passage 2 after 8 days of air liquid interface (ALI) culture. From left to right, inserts were stained with basal cell marker KRT5 and luminal marker KRT8, cilia cell TUBB4B with tight junction protein ZO-1, secretory club cell marker SCGB1A1 with cilia marker TUBB4B and the last panel shows TRP63 positive basal cells with ciliated cell marker FOXJ1. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 30 µm. (c) Resistance measurements of MTEC after different passages and 8 days of ALI (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA (n = 3). (d) Quantification of the percentage of FOXJ1 positive ciliated cells after 8 days of ALI comparing MTEC in passage (P) 0, 1 and 2 (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA (n = 3). (e) qRT-PCR analysis of Foxj1 in MTEC in passage (P) 0, 1 and 2 (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA (n = 4). (f) Representative images and quantification of ciliated cells (FOXJ1) after 8 days or 21 days ALI and with or without the presence of DAPT during differentiation (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA (n = 6). Scale bar, 30 µm.