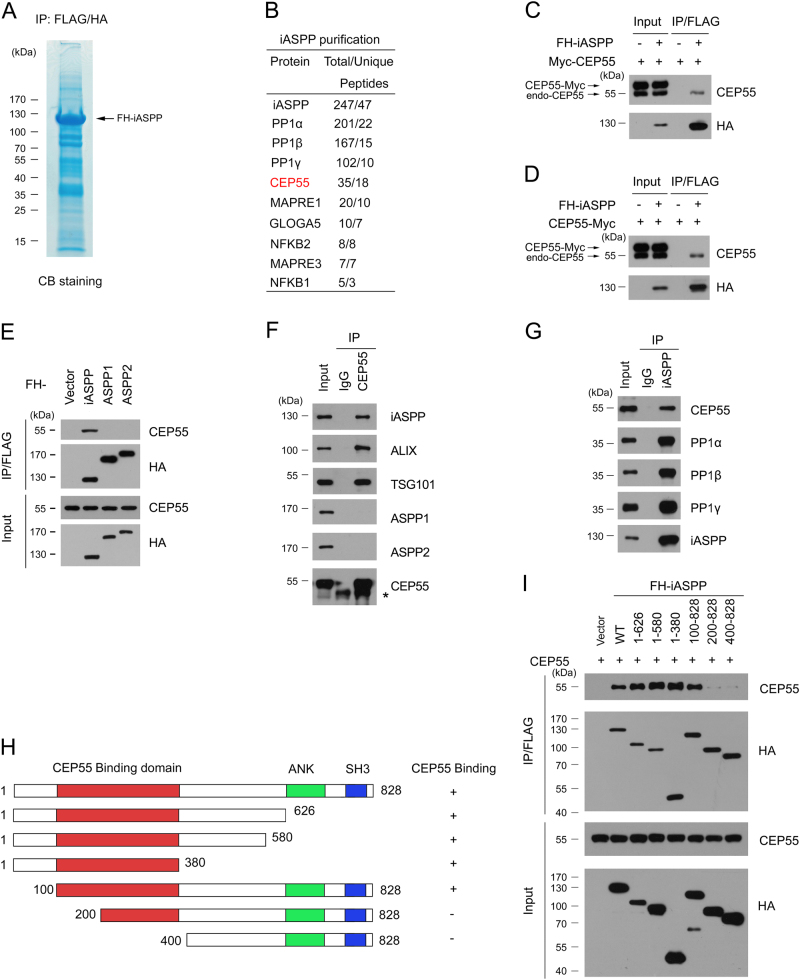
Fig. 1. Identification of CEP55 as a novel iASPP interactor.
a, b Tandem affinity purification of iASPP-containing protein complex was conducted using HeLa cells stably expressing FH-iASPP. Associated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie Blue (CB) staining (a). The number of total/unique peptides identified by mass spectrometry analysis are shown in the table (b). c, d Exogenous overexpressed iASPP interacts with endogenous CEP55, but not the N-terminal (c) or C-terminal (d) Myc-tagged CEP55. 293T cells were co-transfected with indicated constructs. Cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blotting (WB) with indicated antibodies. e Exogenous overexpressed iASPP, but not the ASPP1/2, interacts with CEP55. 293T cells were transfected with indicated constructs. Cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by WB with indicated antibodies. f, g Endogenous iASPP interact with CEP55. Immunoprecipitation using anti-CEP55 (f) or iASPP (g) antibodies were performed using cell lysates prepared from HeLa cells. The immunoprecipitates was detected by WB with indicated antibodies. The asterisk (*) denotes a non-specific band. h Schematic representation of iASPP deletion mutants. Binding capacity of iASPP-WT or mutants to CEP55 is indicated with the symbols. i Identification of CEP55-binding domain in iASPP. 293T cells were transfected with indicated constructs. Cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by WB