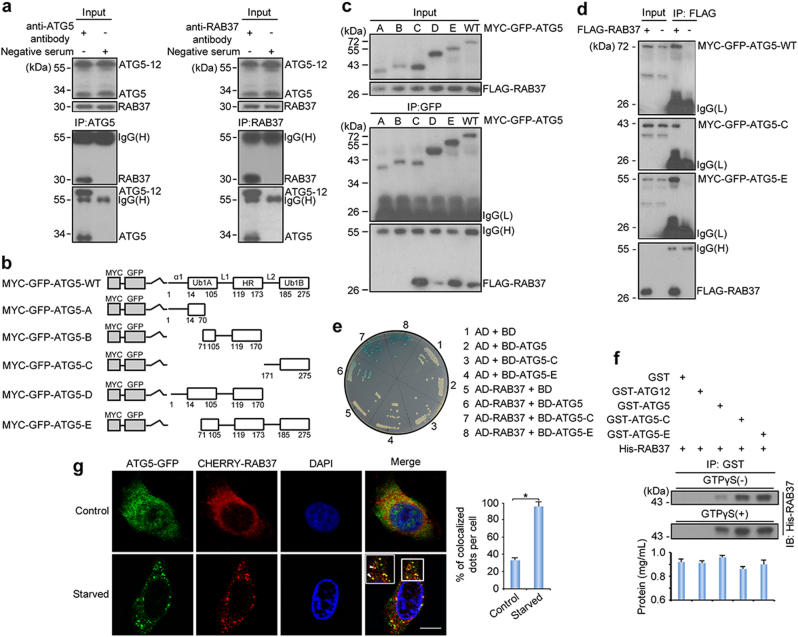
Fig. 1.
RAB37 directly interacts with ATG5. a Co-immunoprecipitation analysis between endogenous RAB37 and ATG5 in 293T cells. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-ATG5, anti-RAB37 antibody or negative serum respectively, followed by immunoblotting with the anti-RAB37 or anti-ATG5 antibody respectively. b A schematic diagram of human ATG5 wild type and deletion mutants. The conserved domains (α1, UblA, L1, HR, L2 and Ub1B) are indicated in wild type ATG5. c, d Interactions of RAB37 with ATG5 mutants. 293T cells were transiently co-transfected with FLAG-RAB37 and MYC-GFP-ATG5 mutants or ATG5 wild type. Cell lysates were examined by Western blotting using an anti-GFP or anti-FLAG antibody. For co-immunoprecipitation assays, the lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-GFP antibody followed by immunoblotting with an anti-FLAG or anti-GFP antibody (c), or immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody followed by immunoblotting with an anti-GFP or anti-FLAG antibody (d). e Identification of the interaction between RAB37 and ATG5 by yeast two-hybrid assay. Y2HGold cells were transformed with plasmids as indicated. The growth of yeast colonies containing relevant plasmids on SD/-His/-Leu/-Trp medium showed that RAB37 interacted with wild-type ATG5, and the truncated ATG5-C and -E in yeast cells. AD, pGADT7; BD, pGBKT7. f In vitro GST-pulldown assay showed interaction of RAB37 with ATG5 and ATG12, which was dependent on GTP binding activity of RAB37. GST-ATG5, GST-ATG5-C, GST-ATG5-E, and GST-ATG12 were incubated with His-tagged RAB37 respectively, when present of GTPγS or not. Proteins pulled down with glutathione-agarose were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with an anti-RAB37 antibody. Bottom: total proteins per lane were determined by the Pierce BCA protein assay kit. g Co-localization of RAB37 puncta with ATG5. COS-7 cells were co-transfected with CHERRY-RAB37 and ATG5-GFP. Before fixation, the cells were cultured in starvation medium EBSS for 1 h. Co-localization dots were observed between CHERRY-RAB37 and ATG5-GFP as indicated in arrowheads. Square areas in white line were enlarged. Images were captured using confocal microscopy. The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Percentage of co-localized dots (CHERRY-RAB37 + ATG5-GFP (yellow) / ATG5-GFP (green)) upon starvation was determined in comparison with non-starvation controls. Data are presented as means ± S.D. * stands for P < 0.05 (n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 10 µm