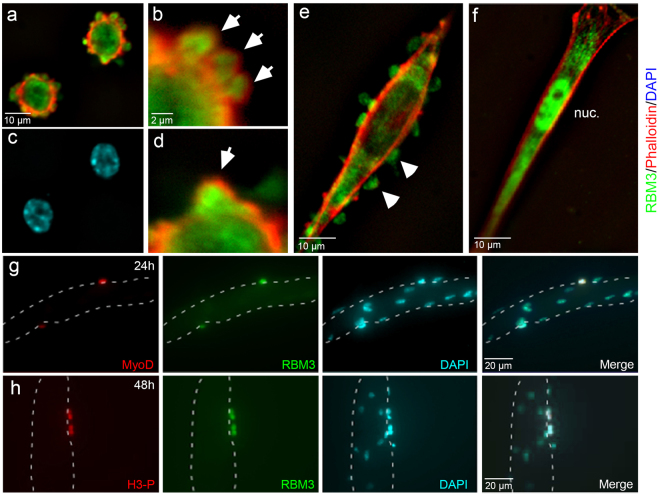
Figure 5.
Dynamic localization of RBM3 in differentiating primary myoblasts. (a) Image of F-actin (red, phalloidin), RBM3 (green) in myoblasts fixed shortly after plating (1 hr) onto fibronectin. SICs are clearly visible along the edges of recently adherent cells as F-actin-delimited outpouchings of membrane. RBM3 is concentrated within SICs. (c) DAPI-stained nuclei in cells from Panel a. (b and d) Blowup of upper and lower margins of cell from the top-right portion of panel A. SICs (arrowheads) can be seen clearly with a peripheral F-actin ring surrounding an RBM3-rich core. (e) Image of a myoblasts partially differentiated into a myotube. At this stage, RBM3 is present in membranous blebs devoid of F-actin that are known to mediate myoblast migration. (f) Image of a fully differentiated satellite cell. RBM3 relocalizes from membrane protrusions to the cytoplasm and nucleus (nuc). (g) Images of a myotube explant at 24 hrs in culture in which activated satellite cells migrating along the myotube border (dashed outline) co-express MyoD (red) and RBM3 (green). (h) Images of dividing satellite cells along the border of a myotube that co-label for histone H3 phosphate (H3-P, red) and RBM3 (green).