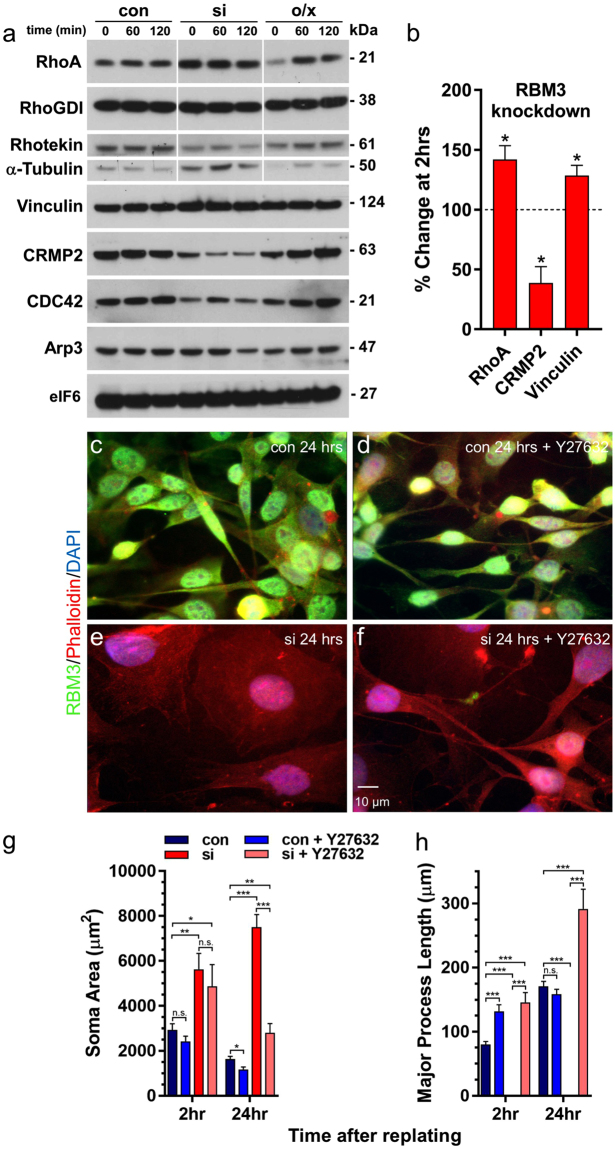
Figure 7.
RBM3-regulated changes in cell morphology involve RhoA-ROCK signaling. (a) Western blots showing expression levels of the indicated proteins at 0, 60, and 120 minutes after replating of B104 cells maintained in control (con), RBM3 knockdown (si), and RBM3 overexpression (o/x) conditions. A large increase in RhoA is observed at all timepoints in RBM3 knockdown cells, along with tubulin and a modest increase in vinculin, an SIC component. CRMP2, rhotekin, and CDC42 were downregulated in the knockdown condition. In cells overexpressing RBM3, RhoA was initially downregulated. (b) Bar graph of changes in RhoA, CRMP2 and vinculin at 2 hrs in RBM3 knockdown vs control cells (n = 4 experiments; *p < 0.05, 1-sample t-test), normalized to eIF6 (present blots) or β-actin (additional experiments, Supplementary Fig. S11). (c–f) Images of RBM3 (green), F-actin (red, phalloidin), and nuclei (blue) in B104 cells under control (con) and RBM3 knockdown conditions (si), with and without the ROCK inhibitor Y27632 (100 μM). Inhibition of ROCK rescued cell polarity in RBM3 knockdown B104 cells (scale bar = 10 μm). (g,h) Graphs summarizing cell body areas (g) and major process lengths (h) at 2 and 24 hrs post replating in the following treatment conditions: control cells (con: n = 17 at 2 hrs; n = 23 at 24 hrs), RBM3 knockdown cells (si: n = 22 at 2 hrs; n = 20 at 24 hrs), control cells treated with Y27632 (con + Y27632: n = 15 at 2 hrs; n = 25 at 24 hrs), RBM3 knockdown cells treated with Y27632 (si + Y27632: n = 12 at 2 hrs; n = 15 at 24 hrs; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005; t-tailed t-test). Cells in which RBM3 was knocked down, but not treated with Y27632, did not have processes to measure.