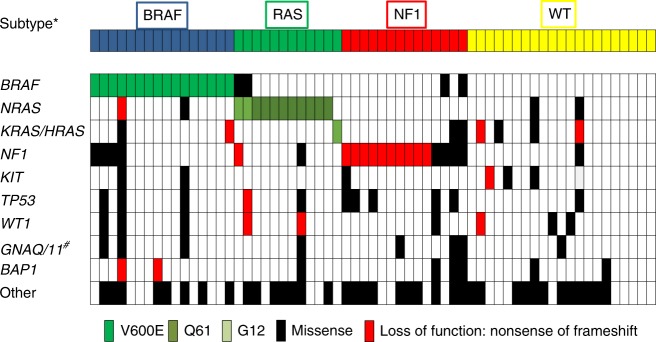
Fig. 1.
Mutations in conjunctival melanoma. Distribution of mutations identified by amplicon panel next-generation sequencing. Green: mutations known or assumed to be activating; Red: nonsense or frameshift loss-of-function mutations; Black: missense mutation with unknown functional consequences. Mutations listed as “Other” include mutations detected in CDK4, FLT4, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, FBXW7, MITF, MAP2K1, MAP2K2, ARID1A, ARID2, SF3B1, CTNNB1, PTEN, CDKN2A, SMARCA4A, EZH2, IDH1 and the protein-coding area of TERT (the promoter region of TERT was not covered by the amplicon-based sequencing panel used in this study). *Subtype according to TCGA genomic classification of cutaneous melanoma. #None of the GNAQ or GNA11 mutations identified were the known activating Q209 or R183 mutations recurrently identified in uveal melanomas (details in Supplemental Table 2)