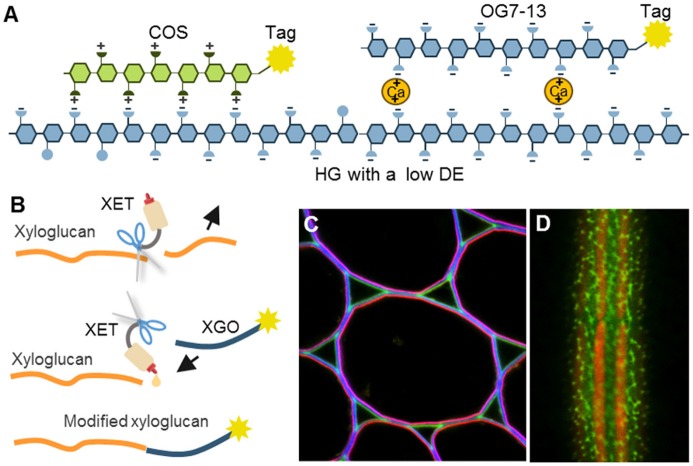
Figure 6.
The mechanisms of oligosaccharide probes and examples of their usage. (A) Homogalacturonan (HG) with a low degree of esterification (DE) can be detected by positively charged chitosan oligosaccharides (COS) or by calcium-mediated complexation to long oligogalacturonides (OG7-13) as a form of artificial egg box formation (Mravec et al., 2014, 2017b). (B) Incorporation of tagged xyloglucan (XGO) oligosaccharides to xyloglucan backbone by an activity of xyloglucan endotransglycosylases (XETs). This can be used to visualize the presence of both, a xyloglucan backbone and XET activity. (C,D) Two examples of in situ usage of COS oligosaccharide probes. (C) Triple labeling of stem parenchyma with COS488 (green), Calcofluor White (blue) and JIM7 antibody (red). Note the specific labeling of the middle lamella and triangular junctions with COS488. (D) Labeling of intricate cell wall structures in single cell green alga Penium margaritaceum with COS488 (green). The red signal is due to chlorophyll autofluorescence. For the original experiments see Mravec et al. (2014).