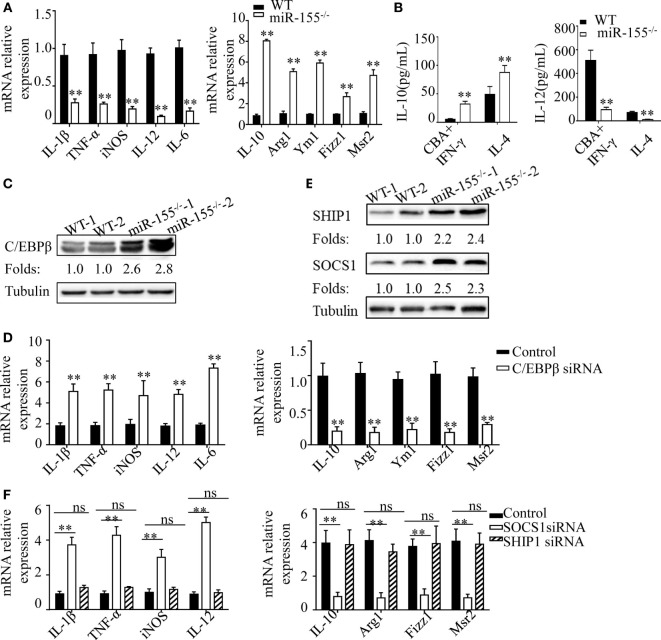
Figure 6.
C/EBPβ and SOCS1 are key functional targets in intestinal M2 polarization. (A) BMDMs isolated from WT and miR-155−/− mice were treated with CBA (10 µg/mL) and IFN-γ (20 ng/mL), and the relative expression of M1genes and M2 genes were determined by Q-PCR. (B) The absolute amounts of secreted cytokines IL-10 and IL-12 (as representative of M2 and M1 gene products, respectively) in the supernatants of WT or miR-155−/− BMDMs that had been treated with M1 condition (CBA + IFN-γ) and M2 condition (IL-4) were measured by ELISA. (C) The protein expression level of C/EBPβ in macrophages (CD11b+CD11c−/low) isolated from LPMCs of dextran sulfate sodium colitis mice were determined by western blotting. (D) miR-155−/− BMDMs were transferred with C/EBPβ siRNA or control and then stimulated with CBA (10 µg/mL) and IFN-γ (20 ng/mL), and the relative expression of M1genes and M2 genes were determined by Q-PCR. (E) The protein expression level of SOCS1 and SHIP1 in macrophages, as described in (C), was determined by western blotting. (F) miR-155−/− BMDMs were transferred with SOCS1 and SHIP1 siRNA and treated as described in (D), and the relative expressions of M1genes and M2 genes were determined by Q-PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs WT control or siRNA control [Student’s t-test in (A,B,D)]. *P < 0.05, ns > 0.05 vs. siRNA control (ANOVA with Bonferroni’s posttest correction for multiple comparisons in (F). Data are representative of three independent experiments (mean and SD). Ns, not significant. BMDMs, bone marrow-derived macrophage. WT, wild-type. CBA, cecal bacterial antigen.