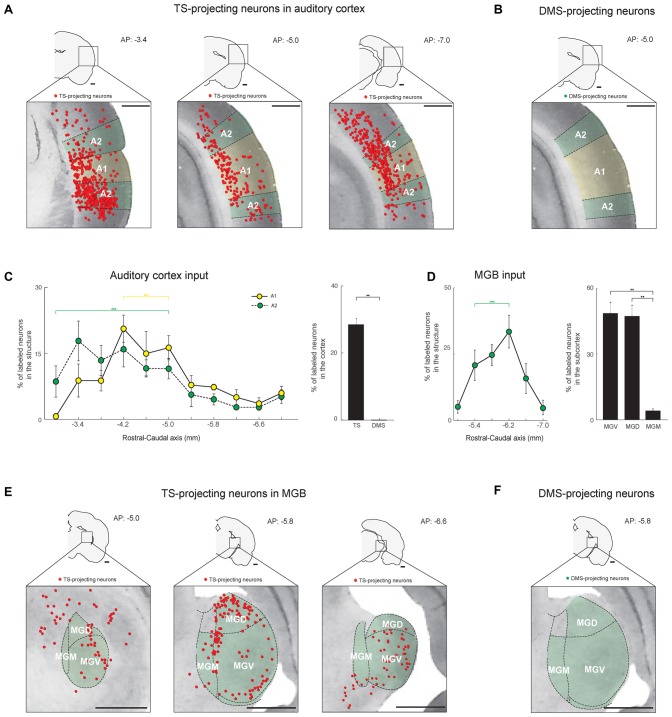
Figure 5.
The TS receives cortical and thalamic auditory inputs: auditory cortex and medial geniculate body (MGB) projections. (A) TS-projecting neurons in the rostral, middle, and caudal parts of the auditory cortex. A1, primary auditory cortex; A2, secondary auditory cortex. (B) DMS-projecting neurons were not found in the auditory cortex. (C) Rostral-caudal distribution of TS-projecting neurons at 400-μm intervals in the subregions of the auditory cortex (left) and proportions of projecting neurons in the cortex (right; TS-projecting neurons, n = 6 hemispheres; DMS-projecting neurons, n = 4 hemispheres). (D) Rostral-caudal distribution of TS-projecting neurons at 400-μm intervals in the MGB (left) and their proportions in the MGB subregions (right; TS-projecting neurons, n = 6 hemispheres). MGB, medial geniculate body; MGV, ventral part of the MGB; MGD, dorsal part of the MGB; MGM, medial part of the MGB. (E) TS-projecting neurons in the rostral, middle, and caudal parts of the MGB. (F) No DMS-projecting neurons were found in the MGB. Scale bars: 1 mm. **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001.