Figure 5.
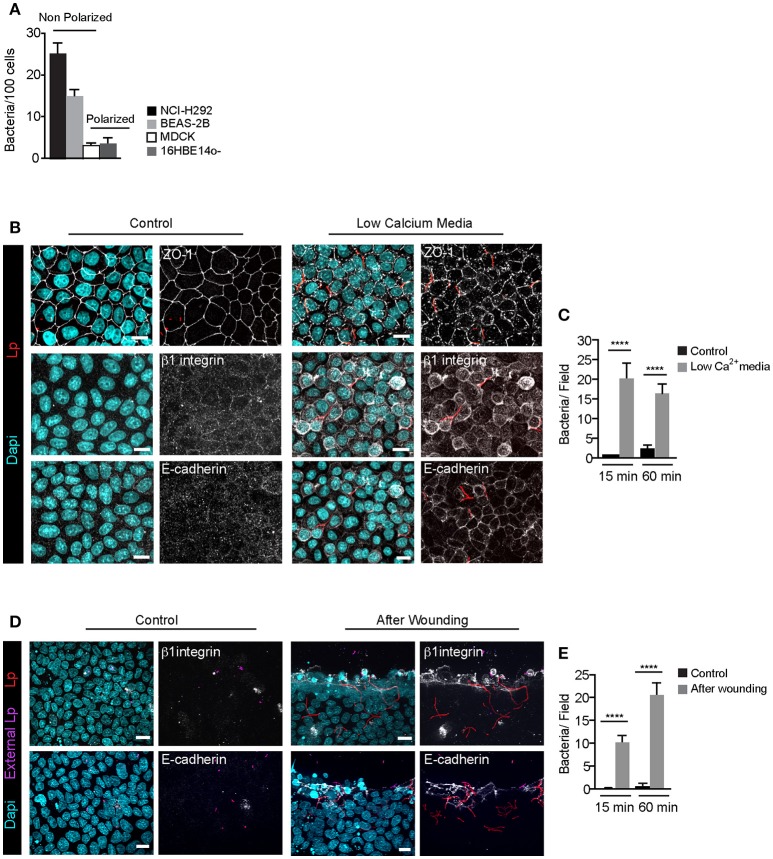
Filamentous Lp do not attach to polarized epithelial cell monolayers (A) Efficiency of Lp attachment to different LECs 1 h p.i. Data shown are means±SEM from 2 independent experiments. Attachment to at least 200 cells was quantified in each experiment. (B) Effect of low calcium media on tight junction permeability. MDCK cell monolayers treated with low calcium media (see Materials and Methods) were infected with RFP-Lp for 15 or 60 min, fixed and external bacteria were immunolabeled (purple). Cells were permeabilized and immunolabeled using anti-Zo1 antibody (top panels), anti-β1 integrin (middle panels) or anti-E-cadherin antibodies (bottom panels). Panels to the left show uninfected control cells. Dapi: cyan. (C) Quantification of Lp attachment to MDCK monolayers after treatment with low calcium media. Data shown are mean ± SEMs from 3 independent experiments. (D) Lp attachment to MDCK cell monolayers after mechanical disruption of tight junctions. Monolayers were wounded and infected with RFP-Lp for 10 or 60 min and fixed. External bacteria and β1 integrin or E-cadherin receptors (grayscale) were immunolabeled in unpermeabilized cells. (E) Quantification of bacterial attachment from (D). Data shown are mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. All scale bars, 12 μm. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test, ****p < 0.0001.