Figure 5.
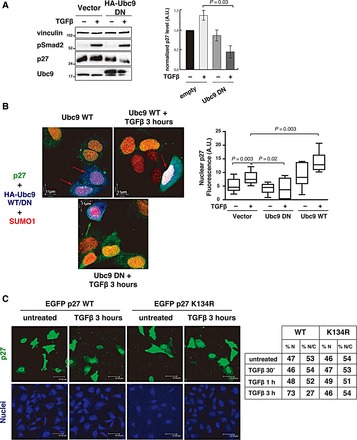
SUMOylation is necessary for TGFβ-induced p27 nuclear accumulation. (A) Western blot analysis of endogenous p27 expression level in MCF7 cells in the presence or absence of HA-tagged dominant-negative Ubc9 vector (HA-tagged Ubc9DN), and treated or not with TGFβ (20 ng/ml) for 3 h. Vinculin was used as loading control and phosphorylated Smad2 (pSer 465/467) was used as a marker of TGFβ signaling activation. Normalized p27 level (p27/vinculin ratio) relative to the level in empty vector-transfected, untreated cells was determined by densitometric analysis of the blots (±SD) (right graph). (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of p27 (green), SUMO1 (red), and Ubc9WT or Ubc9DN (blue) in MCF7 cells transiently transfected with HA-tagged Ubc9WT or Ubc9DN, and treated or not with TGFβ (20 ng/ml) for 3 h. Ubc9-expressing cells were identified using an anti-HA antibody (blue). Red arrows indicate cells expressing Ubc9WT with p27 nuclear accumulation. Green arrow indicates a cell expressing Ubc9DN without p27 nuclear accumulation. Nuclear p27 fluorescence intensity in at least 20 cells expressing or not Ubc9WT or Ubc9DN and treated or not with TGFβ was calculated using the Volocity™ Software (right graph). Significance was calculated using the Mann–Whitney unpaired t-test. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of EGFP-p27 expression and localization (green) in HeLa cells transiently transfected with HA-SUMO1, untagged Ubc9, and EGFP-p27WT or EGFP-p27K134R mutant, and then treated with TGFβ (20 ng/ml) for 3 h. Nuclear staining is reported in blue. The percentage of cells expressing nuclear (%N) or nuclear + cytoplasmic (%N/C) EGFP-p27WT or EGFP-p27K134R before and after 30 min, 1 h, and 3 h of TGFβ treatment was determined (right table). Data were collected by using a 40× objective and scoring all transfected cells in 10 randomly selected fields per each condition.
