Figure 4.
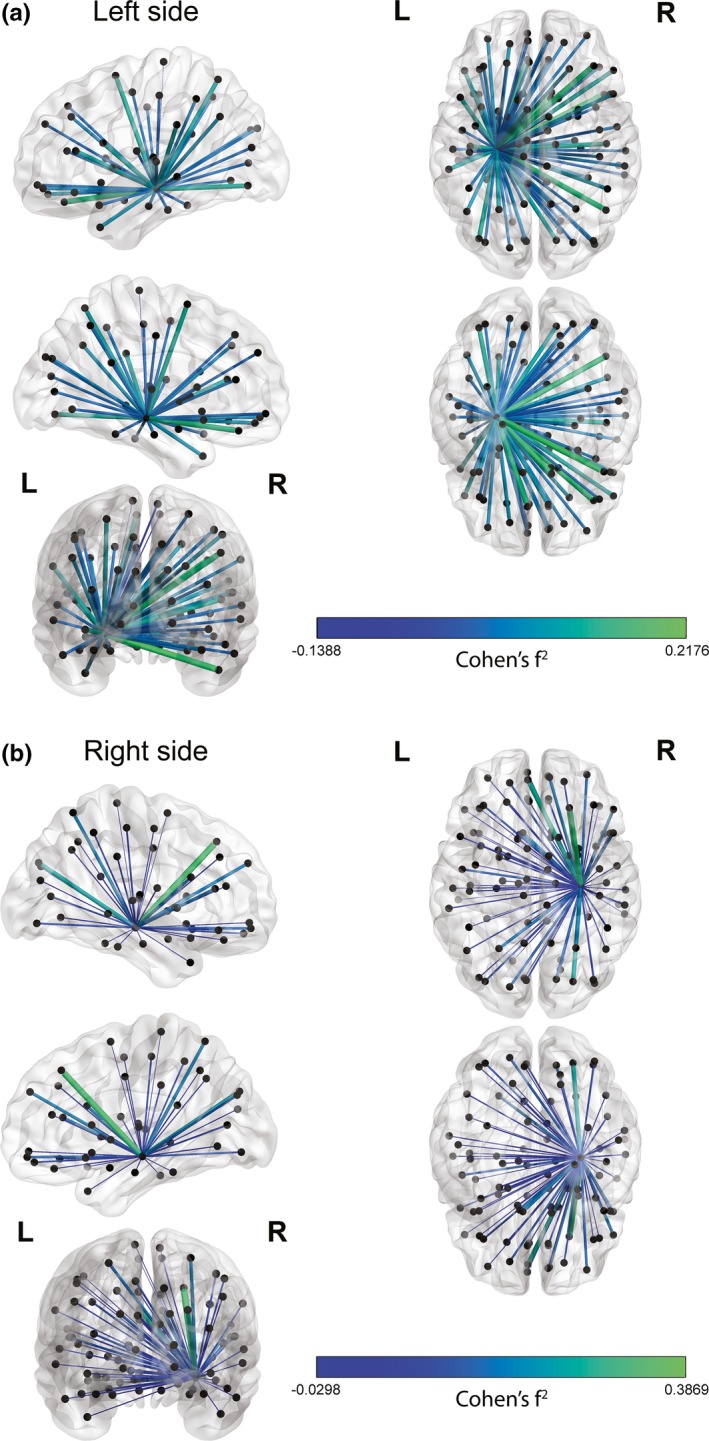
Visualization of spatial importance of dynamic functional connectivity (dFC) for learning and memory in multiple sclerosis. For verbal (a) and visuospatial (b) memory separately, the increase in effect size as a result of adding dFC on top of stationary brain measures (sex and left hippocampal volume for verbal learning and memory, and stationary functional connectivity of the right hippocampus for visuospatial learning and memory) is projected on a glass brain using BrainNet Viewer. A positive value suggests that dFC increases the effect size on top of stationary brain measures, whereas a negative value indicates a decrease in effect size
