Figure 1.
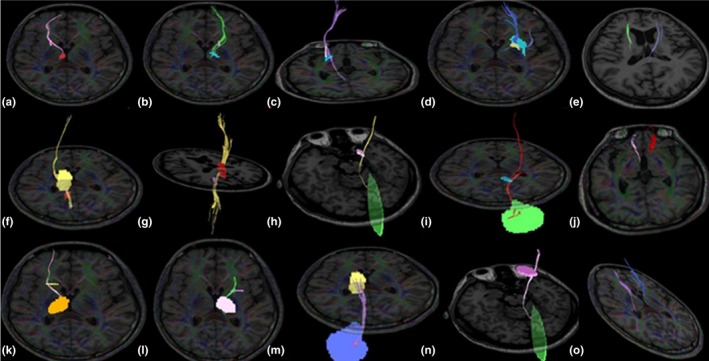
Diffusion tensor imaging results showing the volumes of fiber tracts between ROIs in the brains of patients with WD. The volumes of the left (b) and right (a) fibers between the GP and SN differed (p = .043, asymmetry index = 1.233), the volume of fibers between the GP and PU was lower on the right side (c) than on the left side (d) (p = .035, asymmetry index = 1.413), the volumes of the left and right fibers between the PU and SN differed (e) (p = .044, asymmetry index = 1.260), the volume of fibers between the SN and TH was lower on the right side (f) than on the left side (g) (p = .046, asymmetry index = 1.220), the volume of fibers between the SN and cerebellum was higher on the right side (h) than on the left side (i) (p = .049, asymmetry index = 1.437), the volumes of the left and right fibers between the CA and SN differed (j) (p = .023, asymmetry index = 1.503), the volume of fibers between the CA and TH was higher on the right side (k) than on the left side (l) (p = .037, asymmetry index = 1.145), the volume of fibers between the TH and cerebellum was higher on the right side (m) than on the left side (n) (p = .041, asymmetry index = 1.279), the volumes of the left and right fibers between the PU and CA differed (O) (p = .016, asymmetry index = 1.138). Abbreviations: PU, putamen; ROI, regions of interest; GP, globus pallidus; CA, head of the caudate nucleus; TH, thalamus; SN, substantia nigra; WD, Wilson's disease
