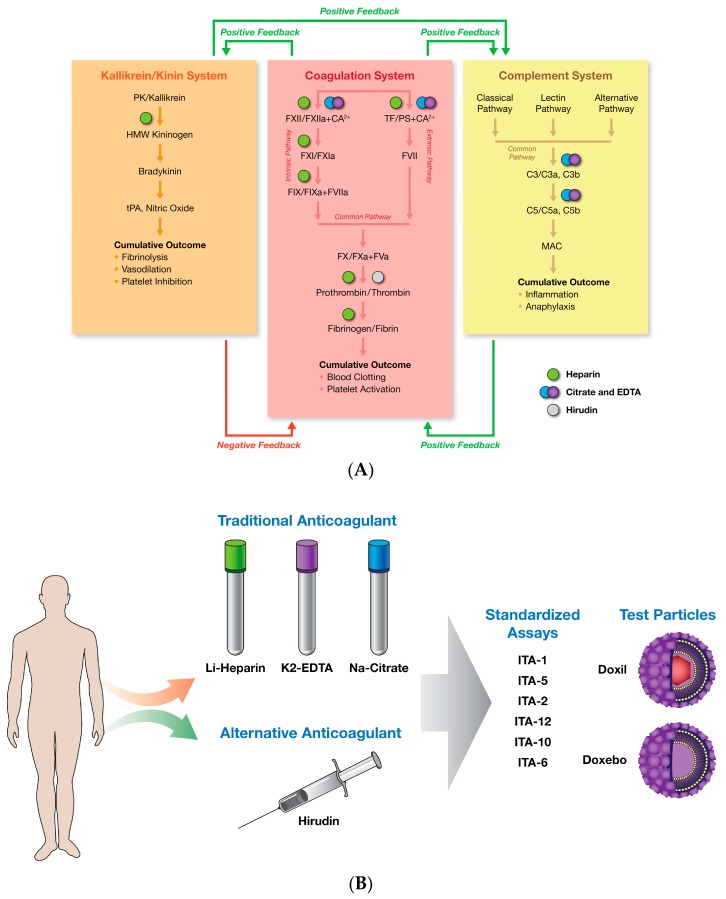
Figure 1.
Rationale and study design. (A) Anticoagulants and their effects on various components of complement, plasma coagulation, and kinin/kallikrein systems are shown in this diagram. There is a cross-talk between these systems. Activation of the coagulation provides positive (i.e., agonist) feedback to the complement and kinin/kallikrein systems. Likewise, activated complement system stimulates coagulation, while activation of kinin/kallikrein system can also activate complement system. Cumulative outcome of the kallikrein/kinin system supplies a negative (i.e., inhibitory) feedback to the coagulation system to stop the blood clotting process and maintain hemostasis. Colored dots representing specific anticoagulant are shown above their respective protein targets. Unlike heparin, citrate, and EDTA, hirudin has a single target affecting only the coagulation cascade; (B) Schematic depiction of the study design. F—factor; C—complement; ITA—immunotoxicity assay from the standardized assay cascade (https://ncl.cancer.gov/resources/assay-cascade-protocols); TF—tissue factor; PS—phosphatidylserine; EDTA—ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid; PK—prekallikrein; tPA—tissue plasminogen activator; HMW—high molecular weight; MAC—membrane attack complex; K2—potassium ions.