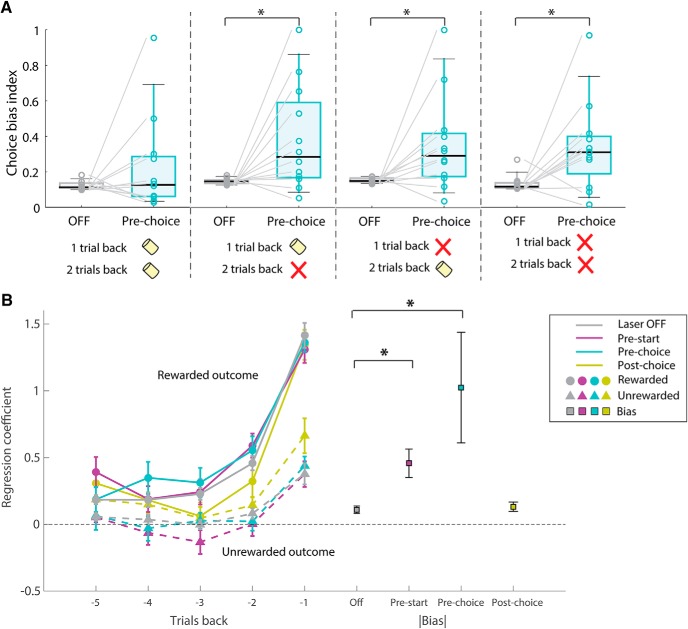
Figure 3.
Effect of mPFC on choice bias depends on outcome history, but mPFC inactivation does not affect the evaluation of outcomes. A, Choice bias indices calculated separately for different past outcomes. Choice bias indices in pre-choice inactivation trials were significantly larger than corresponding choice bias indices for laser off trials if unrewarded trials occurred during the past two trials but not if the two past trials were both rewarded (left). VGAT-ChR2, n = 12 mice, Trial (n − 2) (n − 1) = (Rewarded, Rewarded); median = 0.15 (Laser OFF); 0.29 (Pre-choice), W = 49, p = 1.00 (Trial (n − 2) (n − 1)) = (Unrewarded, Rewarded); median = 0.11 (Laser OFF); 0.13 (Pre-choice), W = 70, p = 0.048 (Trial (n − 2) (n − 1)) = (Rewarded, Unrewarded); median = 0.15 (Laser OFF); 0.29 (Pre-choice), W = 70, p = 0.048 (Trial (n − 2) (n − 1)) = (Unrewarded, Unrewarded); median = 0.12 (Laser OFF); 0.31 (Pre-choice), W = 71, p = 0.037, Wilcoxon signed-rank test for Laser Off versus Pre-choice. p values were multiplied by 4 for Bonferroni's correction of p values. B, Choice was modeled using a logistic regression model with independent variables for outcomes and inactivation types. Regression coefficients for rewarded or unrewarded outcomes were unchanged in pre-start (magenta) and pre-choice inactivation (cyan) compared with corresponding coefficients in laser-off (gray) trials. This indicated that the increased choice bias (squares) induced by pre-start or pre-choice photoinhibition was independent from the processing of reward information. For inactivation conditions, coefficients of choice plus those of choice × laser interaction were plotted (a + c, a + e, a + g, b + d, b + f, b + h; for the labeling of variables, see Materials and Methods). Absolute values of coefficients of bias terms were significantly increased in pre-start and pre-choice inactivation (VGAT-ChR2, n = 12 mice, OFF vs Pre-start, OFF vs Pre-choice). *p < 0.05 (Wilcoxon signed-rank test with Bonferroni's correction of p value).