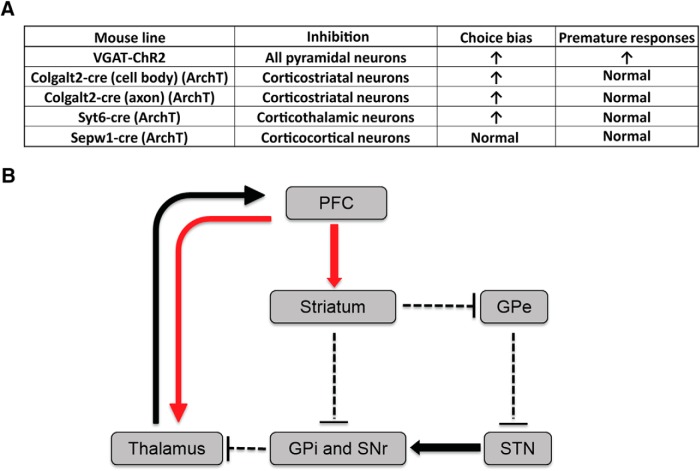
Figure 8.
Summary of anatomical and genetic results and underlying circuits for behavioral flexibility. A, Summary of mouse lines for expression of ChR2 or ArchT in the mPFC, indicating the dominant projection area and the behavioral phenotypes induced by optogenetic stimulation during the probabilistic reversal task. B, Model for the cortico-striato-thalamocortical circuit underlying behavioral flexibility. Adapted with permission from Pauls et al. (2014). Behavioral flexibility was impaired when corticostriatal and corticothalamic deep layer pyramidal neurons (red arrows) were inactivated. GPe, External globus pallidus; GPi, internal globus pallidus; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata.