Figure 2.
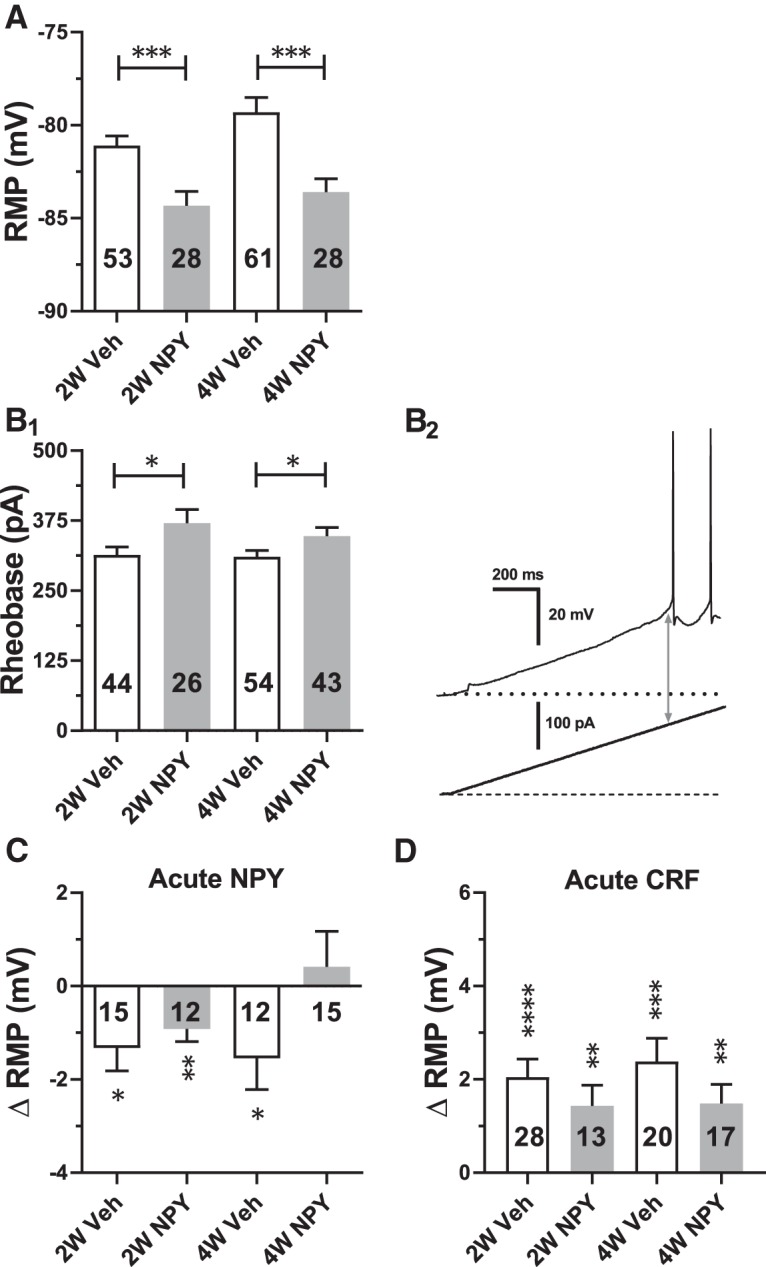
Effects of repeated NPY or Veh treatment on electrophysiological properties of BLA PNs in brain slices taken at 2W and 4W after initiation of treatment. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Numbers of individual neurons tested are indicated in each bar. A, Effect on resting membrane potential (RMP; 2W: t(79) = 3.57, p = 0.0006; NPY: n = 28 cells/24 rats, Veh: n = 53/17 and 4W: t(107) = 3.86, p = 0.0002, NPY: n = 61/30 Veh: n = 48/22). B1, Effect on rheobase (2W: t(68) = 2.16, p = 0.034; NPY: n = 26/16 Veh: n = 44/25 and 4W: t(95) = 1.98, p = 0.04; NPY: n = 43/22, Veh: n = 54/32). B2, Representative current-clamp recording depicting rheobase measurement as magnitude of ramp current (arrow) required to induce action potential firing from rest in a 2W Veh-treated neuron. C, Effect of acute NPY (1 μm) application on RMP as indicated (2W-Veh: t(14) = 2.73, p = 0.016; 2W-NPY: t(11) = 3.44, p = 0.0055; 4W-Veh: t(11) = 2.30, p = 0.042, 4W-NPY: t(14) = 0.54, p = 0.60). Data from 12 rats in each group are shown (ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparisons test F(3,50) = 2.30, p = 0.089). D, Effect of acute CRF (30 nm) application on RMP as indicated (2W-Veh: t(27) = 5.30, p = 1.35e-5; 2W-NPY: t(12) = 3.20, p = 0.0076; 4W-Veh: t(19) = 4.77, p = 0.0001, 4W-NPY: t(16) = 3.595, p = 0.0024). Data from 9–17 rats in each group are shown (ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparisons test F(3,74) = 0.96, p = 0.42). A, B, Unpaired t tests; C, D, paired-t tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
