Figure 2.
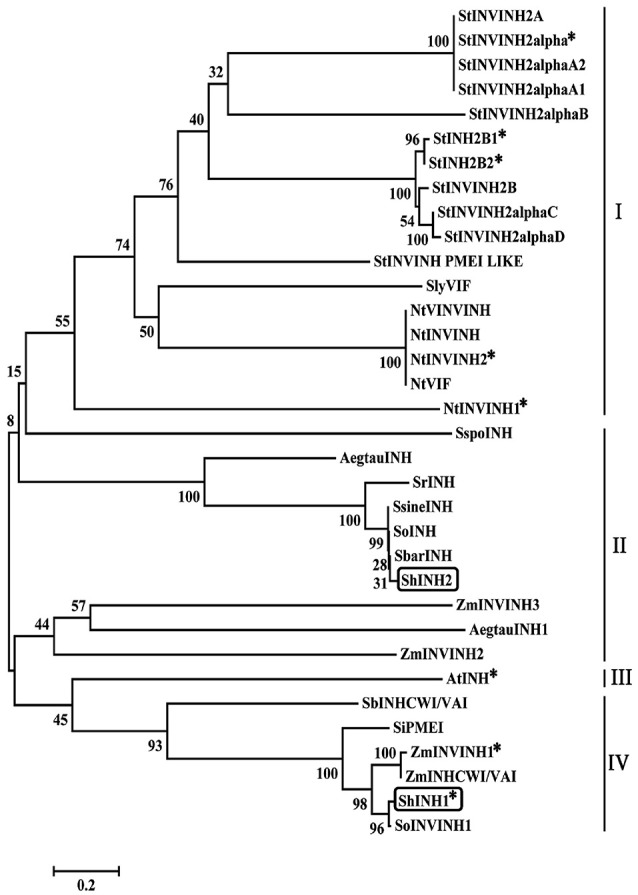
Phylogenetic relationships of plant INVINH proteins. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by neighbor joining using aligned INVINH sequences analyzed by MEGA7.0. Asterisk (*) indicates invertase inhibitors characterized experimentally. ShINH1 & ShINH2 are shown in boxes. Dicot (I and III) and monocot (II and IV) INVINH proteins alignment are shown in lines. INVINH-like proteins from Solanum tuberosum (StINVINH2A, GU321341; StINVINH2α, KJ788176; StINVINH2αA2, FJ810206; StINVINH2αA1, FJ810205; StINVINH2αB, FJ810207; StINVINH2b1, ADZ54776; StINVINH2b2, GU980595; StINVINH2B, GU321342; StINVINH2αC, FJ810208; StINVINH2αD, FJ810209; StINVINH PMEI LIKE,); Solanum lycopersicum, (KC007445); Nicotiana tobacum (NtVINVINH, AY145781; NtINVINH, AY594179; NtINVINH2, Y12805; NtVIF, AAN60076; NtINVINH1, Y12806); S. spontaneum (SspoINH, KP844455); Aegilops tautschi (AegtauINH, XM_020320985); S. robustum (SrINH, KP055631); S. sinense (SsineINH, KP997206); S. officinarum (SoINH, KP997207); S. barberi (SbarINH, KU057162); Saccharum hybrid (ShINH2, MG457817); Zea mays (ZmINVINH3, CAC69343); A. tautschi (AegtauINH1, XM_020311699); Z. mays (ZmINVINH2, CAC69336); Arabidopsis thaliana (AtINH, Y12807); Sorghum bicolor (SbINHCWI/VAI, XM_002446958.2); Setaria indica (SiPMEI, XM_004978185.1); Z. mays (ZmINVINH1; ZmINHCWI/VAI, XM_008670754.2) and Saccharum hybrid (ShINH1, MG457818; SoINVINH1, KF575171;). A total of 1,000 bootstrapping runs were performed and % reliability is labeled next to each branch. ShINH1 and ShINH2 clustered within the Saccharum spp. and were closely related to monocot INVINH proteins.
