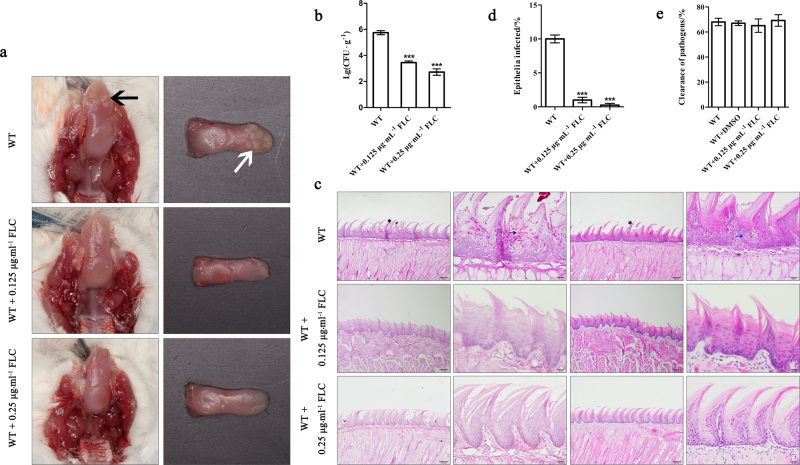
Fig. 4.
FLC can cure the epithelial infection caused by C. albicans at low dosage in vivo. a Images of infected mice tongues with oral candidal leukoplakia after 2-day oropharyngeal infection with wild type (WT) strain drinking water with or without different doses of FLC. Leukoplakia on tongue are indicated in vivo by black arrow while showed by white arrow on incided tissue. b Fungal burdens obtained from the tongues of mice after 2-day oropharyngeal infection with C. albicans WT strain with or without FLC. c PAS- and HE-stained tongues from mice 2 days post infection by C. albicans. Including whole-mount and high-magnification views infected by WT with or without different doses of FLC. Invading hyphae are indicated by black arrowhead and inflammatory cells are showed by blue arrowhead. d Average percentage of the mice entire tongue epithelium area infected by WT strain. e Susceptibility of C. albicans to macrophagocyte with or without different doses of FLC. FLC fluconazole, PAS Periodic Acid-Schiff, HE hematein eosin