Fig. 4. Oncogenic effects of the HIF2A mutants in vivo.
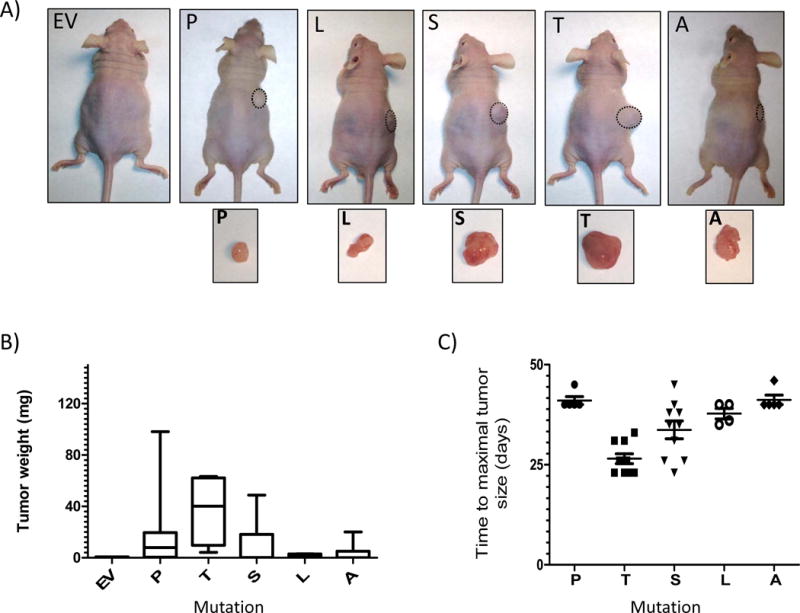
Forty-two nude mice (n=6 or 7 per group) were subcutaneously injected with 5×106 HEK293 cells stably expressing the indicated constructs (empty vector=EV, Pro531Thr=T, Pro531Leu=L, Pro531Ser=S, Pro531Ala=A) or a wild-type Pro531 (P) HIF2A construct. Animals were sacrificed after 28 days and tumors were removed. A) Representative mice and respective tumors are shown. None of the EV-injected mice developed tumors within the observed period. B) Weight (in mg) of tumors plotted by the type of mutation (*EV vs. T p<0.05 by Kruskal Wallis). C) Two additional cohorts (n= 5-10 mice per group) were used and animals were sacrificed when tumors reached maximum size in accordance with IACUC approved protocols. Mice that did not develop tumors were excluded from this analysis. Time from injection until maximum size (in days) was plotted (*P vs. T, and *P vs. S p<0.05).
