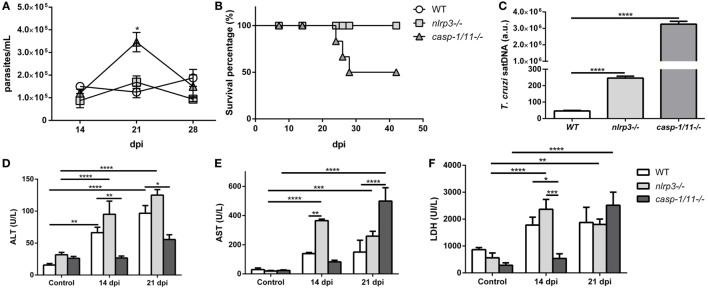
Figure 6.
Caspase-1/11 signaling is required for controlling Trypanosoma cruzi infection but contributes to liver inflammation. Wild type (WT), nlrp3−/−, and caspase-1/11−/− mice were i.p. inoculated with 103 trypomastigotes-Tulahuen strain. (A) Parasitemia levels were examined microscopically at the indicated time points. (B) Survival percentages from infected WT and KO mice up to 42 days post infection (dpi). (C) Hepatic parasitic load was determined by qPCR of satDNA of T. cruzi relative to TaqMan endogenous control and expressed as arbitrary units (a.u.) from infected WT, nlrp3−/−, and caspase-1/11−/− mice at 21 dpi. Activity levels of (D) ALT, (E) AST transaminases, and (F) LDH in plasma are obtained at 14 and 21 dpi. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from one of three representative experiments; n = 3–6 mice per group. Statistical significance was evaluated by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.