Figure 4.
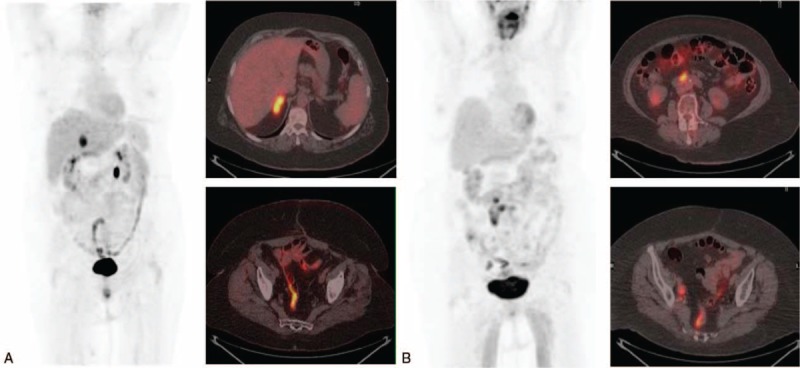
(A) Maximum intensity projection (MIP) and axial fusion positron emission tomography/computed tomography with 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose ([18F]FDG-PET/CT) in a 68-year-old woman with recurrent ovarian cancer (FIGO stage IIIC, high-grade serous carcinoma, diagnosed 49 months before), with CA125 of 51.6 U/mL, CA125vel of 4.6 U/mL per mo and a doubling time of 7.4. Surgery confirmed the existence of a metastasis on right adrenal gland that showed high [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 10.6). (B) Woman (70-year-old) with history of mucinous ovarian carcinoma, that showed rising CA125 (62.4 U/mL), with a CA125vel of 5.4 U/mL per mo and CA125dt of 6.73. The [18F]FDG-PET/CT, MIP, and axial fusion PET/CT exhibited multiple lymph nodes in retroperitoneal space and both iliac territories. All locations visualized in [18F]FDG-PET/CT, with an SUVmax of 7.3, were confirmed histologically. Both cases showed irregular intestinal uptake.
