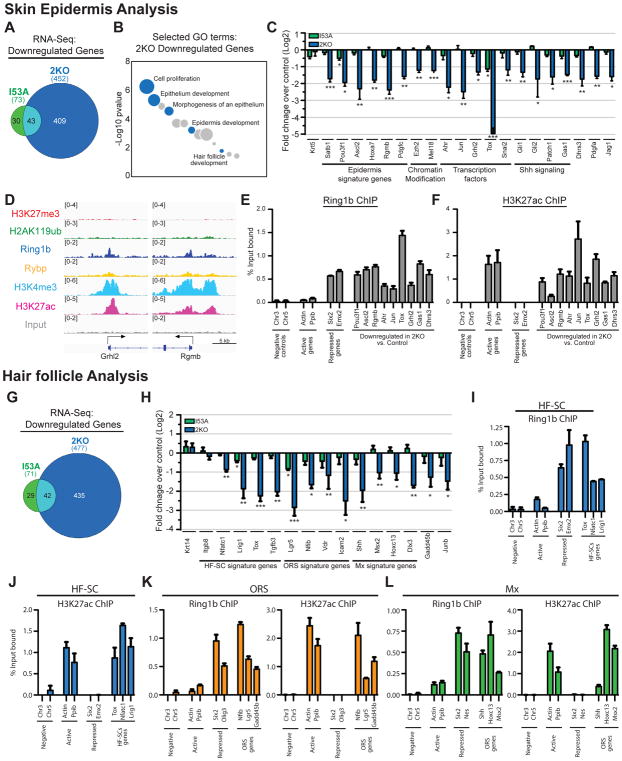
Figure 4. PRC1 is required for the expression of epidermal and hair follicle developmental genes.
(A) Overlap of significantly downregulated genes between I53A and 2KO epidermis. (B) GO analysis of downregulated genes in 2KO epidermis. Selected GO terms are in blue. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of critical epidermal genes in FACS-enriched 2KO and I53A epidermal cells. n=3. (D) IGV browser views of ChIP-seq of Ring1b, H2AK119ub, H3K27me3, H3K27ac, H3K4me3, Rybp, and input for indicated genes in control epidermal progenitors. (E–F) ChIP-qPCR showing the binding of Ring1b (E) and H3K27ac (F) in control epidermal progenitors. Data are mean ±SEM, n=2. (G) Overlap of significantly downregulated genes between I53A and 2KO hair follicle cells. (H) RT-qPCR analysis of hair follicle lineage genes in 2KO and I53A HFs. n=3. (I–L) ChIP-qPCR showing the binding of Ring1b and H3K27ac to hair follicle lineage genes in hair follicle stem cells (HF-SC; I-J), outer root sheath cells (ORS; K), and matrix/transient amplifying cells (Mx; L). Data are mean ±SEM, n=2. Data in graphs (C and H) are mean ±SEM. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 (two-sided t test). See also Figure S5 and Tables S2 and S3.