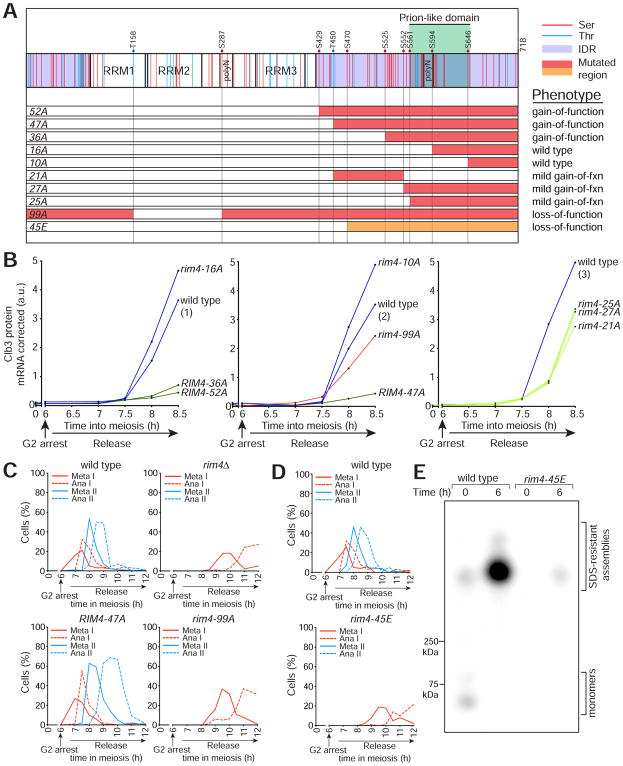
Figure 4. Rim4 clearance is regulated by multi-site phosphorylation.
(A) Diagram of Rim4 with serine and threonine residues denoted in red and blue, respectively. The IDRs are shaded in purple. Mutations contained in each RIM4 phospho-mutant allele are shaded in red or orange (S/T → A and S/T → E respectively). Translational control phenotypes (determined from (B)) are indicated on the right.
(B) CLB3 translational control analysis of RIM4 phospho-mutant alleles. Strains harboring pGAL-NDT80, GAL4.ER, CLB3-3HA, and one of the following: RIM4-3V5 (wild type, blue, B48), rim4-99A-3V5 (red, A30860), RIM4-52A-3V5 (green, B67), RIM4-47A-3V5 (green, A38075), RIM4-36A-3V5 (green, B70), RIM4-27A-3V5 (light green, B152), RIM4-25A-3V5 (light green, B155), RIM4-21A-3V5 (light green, B129), rim4-16A-3V5 (blue, B73), or rim4-10A-3V5 (blue, A38072) were induced to sporulate 30°C. After 6 hours, cells were released from the G 2 arrest. Four strains were run per experiment, each containing a RIM4-3V5 (wild-type) control and three mutant strains. Clb3 protein levels corrected for CLB3 mRNA level are plotted on the y-axis and time in meiosis is plotted on the x-axis. Western and Northern blot source data is shown in Figure S4. (C–E) rim4-99A and rim4-45E are loss of function alleles. (C, D) Strains harboring pGAL-NDT80, GAL4.ER, CLB3-3HA, and one of the following: RIM4-3V5 (wild type, B48), rim4Δ (B343), RIM4-47A-3V5 (A38075), rim4-99A-3V5 (A30860), and rim4-45E-3V5 (B346) were induced to sporulate at 30°C. After 6 hours, cells were released from the G2 arrest. Meiotic progression was analyzed by tubulin IF (n = 100 cells for each time point). (E) Rim4 SDS-resistant assemblies were analyzed by SDD-AGE in RIM4-3V5 (wild type) and rim4-45E-3V5 cells.